Access control¶
Changed in version 3.0: Before Weblate 3.0, the privilege system was based on Django, but is now specifically built for Weblate. If you are using anything older, please consult the documentation for the specific version you are using.
Weblate comes with a fine-grained privilege system to assign user permissions for the whole instance, or in a limited scope.
The permission system is based on groups and roles, where roles define a set of permissions, and groups assign them to users and translations, see Users, roles, groups and permissions for more details.
After installation a default set of groups are created, and you can use those to assign users roles for the whole instance (see Default groups and roles). Additionally when Project access control is turned on, you can assign users to specific translation projects. More fine-grained configuration can be achieved using Custom access control.
Common setups¶
Locking down Weblate¶
To completely lock down your Weblate, you can use REQUIRE_LOGIN to
force users to sign in and REGISTRATION_OPEN to prevent new
registrations.
Site wide permissions¶
To manage permissions for a whole instance, just add users to Users (this is done by default using the Automatic group assignments), Reviewers and Managers groups. Keep all projects configured as Public (see Project access control).
Per project permissions¶
Note
This feature is unavailable for the projects running Libre plan on Hosted Weblate.
Set your projects to Protected or Private, and manage users per project in the Weblate interface.
Custom permissions for languages, components or projects¶
Note
This feature is unavailable for the projects running Libre plan on Hosted Weblate.
Members are granted any permissions assigned to groups they are in, so you can grant the user multiple permissions at once. Create groups and attach them to a project, component, or language. You can put users in multiple groups, and permissions can overlap between them.
Granting any selected permissions based on project, component or language set. To achieve this, create a new group (e.g. Czech translators) and configure it for a given resource. Any assigned permissions will be granted to members of that group for selected resources.
This will work just fine without additional setup, if using per project permissions. For permissions on the whole instance, you will probably also want to remove these permissions from the Users group, or change automatic assignment of all users to that group (see Automatic group assignments).
See also
Project access control¶
Note
By turning on access control, all users are prohibited from accessing anything within a given project, unless you add the permissions for them to do just that.
Note
This feature is unavailable for the projects running Libre plan on Hosted Weblate.
Limit user’s access to individual projects by selecting a different access control variation on the Access tab in the Settings of each respective project. This automatically creates several groups for the project in question, see Predefined groups.
Access control can be set to:
- Public
Publicly visible, translatable for all logged-in users
- Protected
Publicly visible, but translatable only for selected users
- Private
Visible and translatable only for selected users
- Custom
Django admin manages users instead of Weblate, see Custom access control.
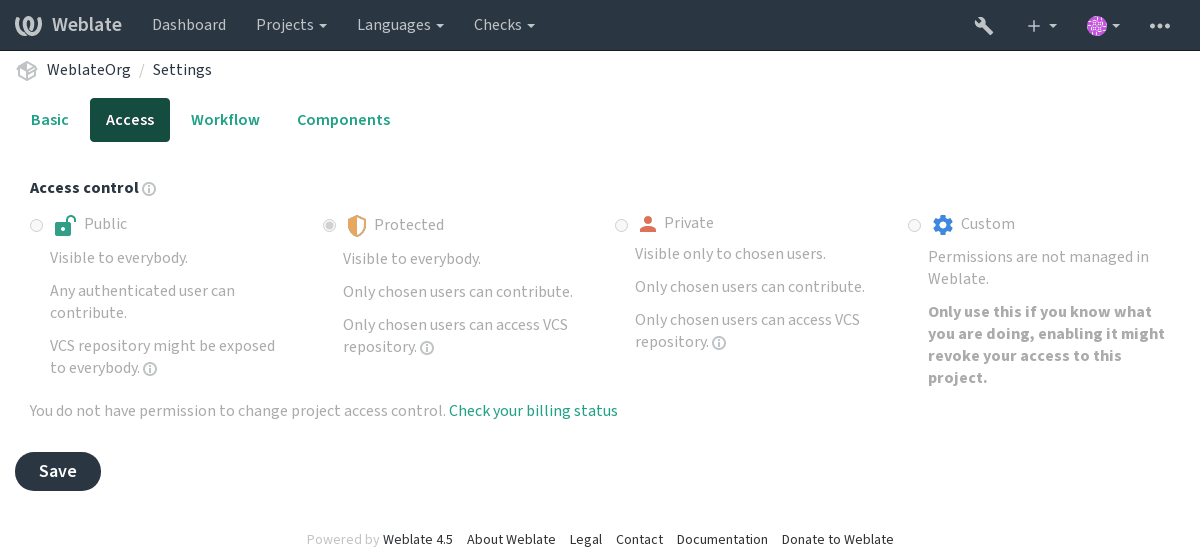
Grant access to a project by adding the privilege either directly to an user, or group of users in the Django admin-interface, or by using user management on the project page, as described in Managing per-project access control.
Note
Even with access control turned on, some info will be available about your project:
Statistics for the whole instance, including counts for all projects.
Language summary for the whole instance, including counts for all projects.
Automatic group assignments¶
From the Authentication in the Django admin interface, users can be assigned to groups [you want this for] automatically based on their e-mail addresses. This only happens upon account creation.
Note
Automatic group assignment to Users and Viewers is always
recreated during migrations. If you want to turn it
off, set the regular expression to ^$ (which will never match).
Users, roles, groups and permissions¶
The authentication models consist of several objects:
- Permission
Individual permissions defined by Weblate. Permissions can not be assigned to users. This can only be done through assignment of roles.
- Role
A Role defines a set of permissions. This allows reuse of these sets in several places, making the administration easier.
- User
Users can belong to several groups.
- Group
Groups connect roles, users and authentication objects (projects, languages and component lists).
Permission checking¶
Whenever a permission is checked to decide whether one is able to perform a given action, the check is carried out according to scope, and the following checks are performed in this order:
The group Component list is matched against accessed component or project (for project-level access).
The group Components is matched against accessed component or project (for project-level access).
The group Projects is matched against accessed project.
Thus, granting access to a component gives the user access to the project it is in too.
Note
Only the first rule will be used. So if you set all of Component list, Components and Project, only Component list will be applied.
An additional step is performed if checking permission for the translation:
The group Languages is matched against accessed translations, it is ignored for component- or project-level access.
Hint
Use Language selection or Project selection to automate inclusion of all languages or projects.
Checking access to a project¶
A user has to be a member of a group linked to the project, or any component inside that project. Having membership is enough, no specific permissions are needed to access the project (this is used in the default Viewers group, see Default groups and roles).
Checking access to a component¶
A user can access the unrestricted component once able to access the containing project. With Restricted access turned on, access to the component requires explicit permission to that component (or a component list it is in).
Managing users and groups¶
All users and the various groups they are in can be managed using the
Django admin interface available, which you can get to by appending
/admin/ to the Weblate site URL.
Managing per-project access control¶
Note
This feature only works for projects using access control, see Project access control.
Users with the Manage project access privilege (see Access control) can also manage users in projects with access control turned on through the project page. The interface allows you to:
Add existing users to the project
Invite new users to the project
Change user permissions
Revoke user access
New in version 3.11.
Resend the e-mail for user invitations (invalidating any previously sent invitation)
User management is available in the Manage menu of any project:
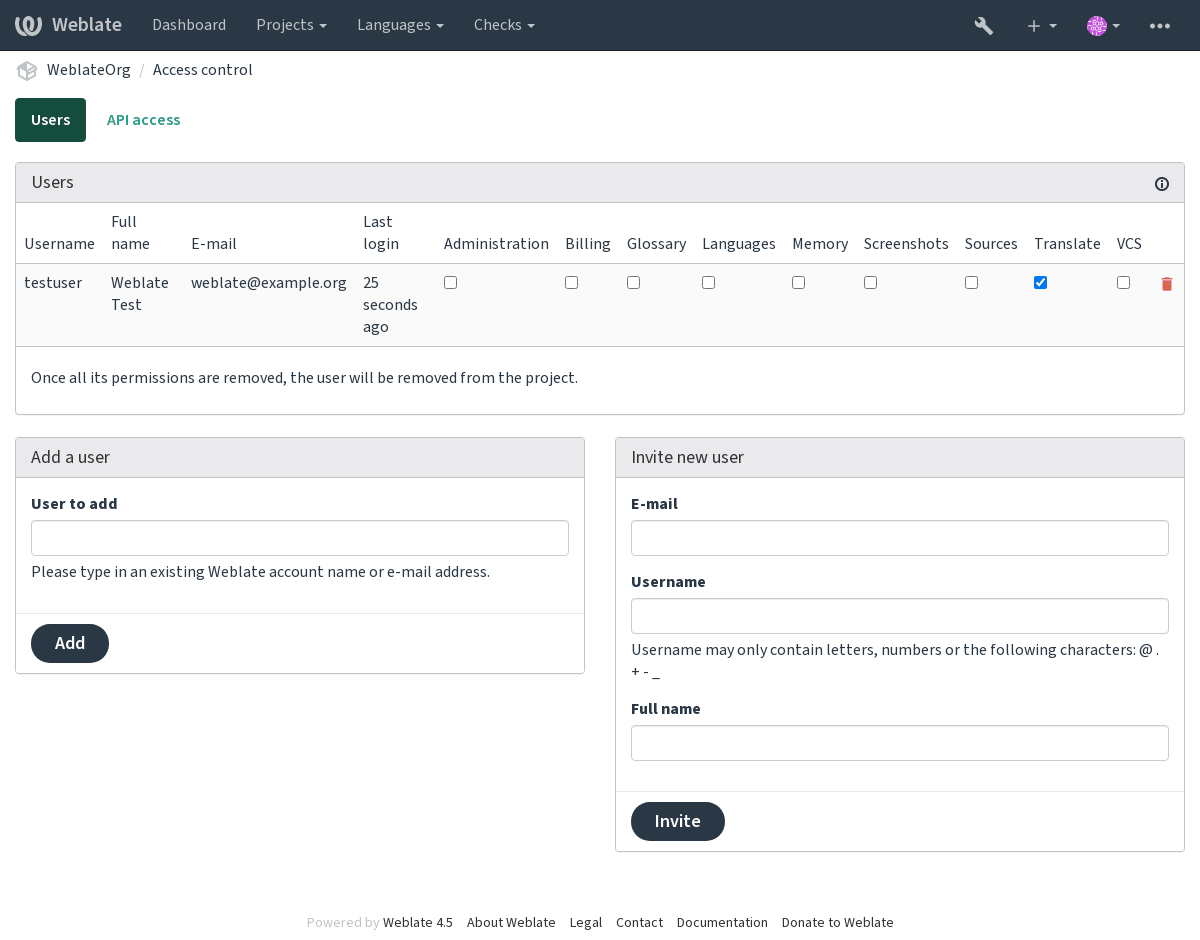
See also
Predefined groups¶
Weblate comes with a predefined set of groups for a project, wherefrom you can assign users.
-
Translate Can translate the project, and upload translations made offline.
-
Sources Can edit source strings in Monolingual components and source string info.
-
Languages Can manage translated languages (add or remove translations).
-
Glossary Can manage glossary (add or remove entries, or upload).
-
Memory Can manage translation memory.
-
Screenshots Can manage screenshots (add or remove them, and associate them to source strings).
-
Review Can approve translations during review.
-
VCS Can manage VCS and access the exported repository.
-
Administration Has all permissions available in the project.
-
Billing Can access billing info (see Billing).
Custom access control¶
To gain more access control adjustments in a project, you can set Access control to Custom to switch over to using the Django admin-interface instead of the one in Weblate.
If you want to do this by default for all current and new projects, configure the
DEFAULT_ACCESS_CONTROL to administrate all permissions and relations using
the Django admin interface.
Warning
By turning this on, Weblate will remove all Project access control it has created for this project. If you are doing this without admin permission from the instance, you will instantly lose your access to manage the project.
Default groups and roles¶
These roles and groups are created upon installation. The built-in roles are always kept up to date by the database migration when upgrading. Custom changes are not lost. Please define a new role if you want to define your own set of permissions.
List of privileges¶
- Billing (see Billing)
View billing info [Administration, Billing]
- Changes
Download changes [Administration]
- Comments
Post comment [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Delete comment [Administration]
- Component
Edit component settings [Administration]
Lock component, preventing translations [Administration]
- Glossary
Add glossary entry [Administration, Manage glossary, Power user]
Edit glossary entry [Administration, Manage glossary, Power user]
Delete glossary entry [Administration, Manage glossary, Power user]
Upload glossary entries [Administration, Manage glossary, Power user]
- Automatic suggestions
Use automatic suggestions [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
- Translation memory
Edit translation memory [Administration, Manage translation memory]
Delete translation memory [Administration, Manage translation memory]
- Projects
Edit project settings [Administration]
Manage project access [Administration]
- Reports
Download reports [Administration]
- Screenshots
Add screenshot [Administration, Manage screenshots]
Edit screenshot [Administration, Manage screenshots]
Delete screenshot [Administration, Manage screenshots]
- Source strings
Edit additional string info [Administration, Edit source]
- Strings
Add new string [Administration]
Remove a string [Administration]
Ignore failing check [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Edit strings [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Review strings [Administration, Review strings]
Edit string when suggestions are enforced [Administration, Review strings]
Edit source strings [Administration, Edit source, Power user]
- Suggestions
Accept suggestion [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Add suggestion [Administration, Edit source, Add suggestion, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Delete suggestion [Administration, Power user]
Vote on suggestion [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
- Translations
Add language for translation [Administration, Power user, Manage languages]
Perform automatic translation [Administration, Manage languages]
Delete existing translation [Administration, Manage languages]
Add several languages for translation [Administration, Manage languages]
- Uploads
Define author of uploaded translation [Administration]
Overwrite existing strings with upload [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
Upload translations [Administration, Edit source, Power user, Review strings, Translate]
- VCS
Access the internal repository [Administration, Access repository, Power user, Manage repository]
Commit changes to the internal repository [Administration, Manage repository]
Push change from the internal repository [Administration, Manage repository]
Reset changes in the internal repository [Administration, Manage repository]
View upstream repository location [Administration, Access repository, Power user, Manage repository]
Update the internal repository [Administration, Manage repository]
- Site wide privileges
Use management interface
Add new projects
Add language definitions
Manage language definitions
Manage groups
Manage users
Manage roles
Manage announcements
Manage translation memory
Manage component lists
Note
Site-wide privileges are not granted to any default role. These are powerful and quite close to superuser status. Most of them affect all projects in your Weblate installation.
List of groups¶
The following groups are created upon installation (or after executing
setupgroups) and you are free to modify them. The migration will
however re-create them if you delete or rename them.
- Guests
Defines permissions for non-authenticated users.
This group only contains anonymous users (see
ANONYMOUS_USER_NAME).You can remove roles from this group to limit permissions for non-authenticated users.
Default roles: Add suggestion, Access repository
- Viewers
This role ensures visibility of public projects for all users. By default all users are members of this group.
By default Automatic group assignments makes all new accounts members of this group when they join.
Default roles: none
- Users
Default group for all users.
By default Automatic group assignments makes all new accounts members of this group when they join.
Default roles: Power user
- Reviewers
Group for reviewers (see Translation workflows).
Default roles: Review strings
- Managers
Group for administrators.
Default roles: Administration
Warning
Never remove the predefined Weblate groups and users, as this can lead to unexpected problems. If you have no use for them, you can removing all their privileges instead.