Verificações e correções¶
As verificações de qualidade ajudam a apanhar erros comuns do tradutor, garantindo que a tradução esteja em boa forma. As verificações podem ser ignoradas em caso de falsos positivos.
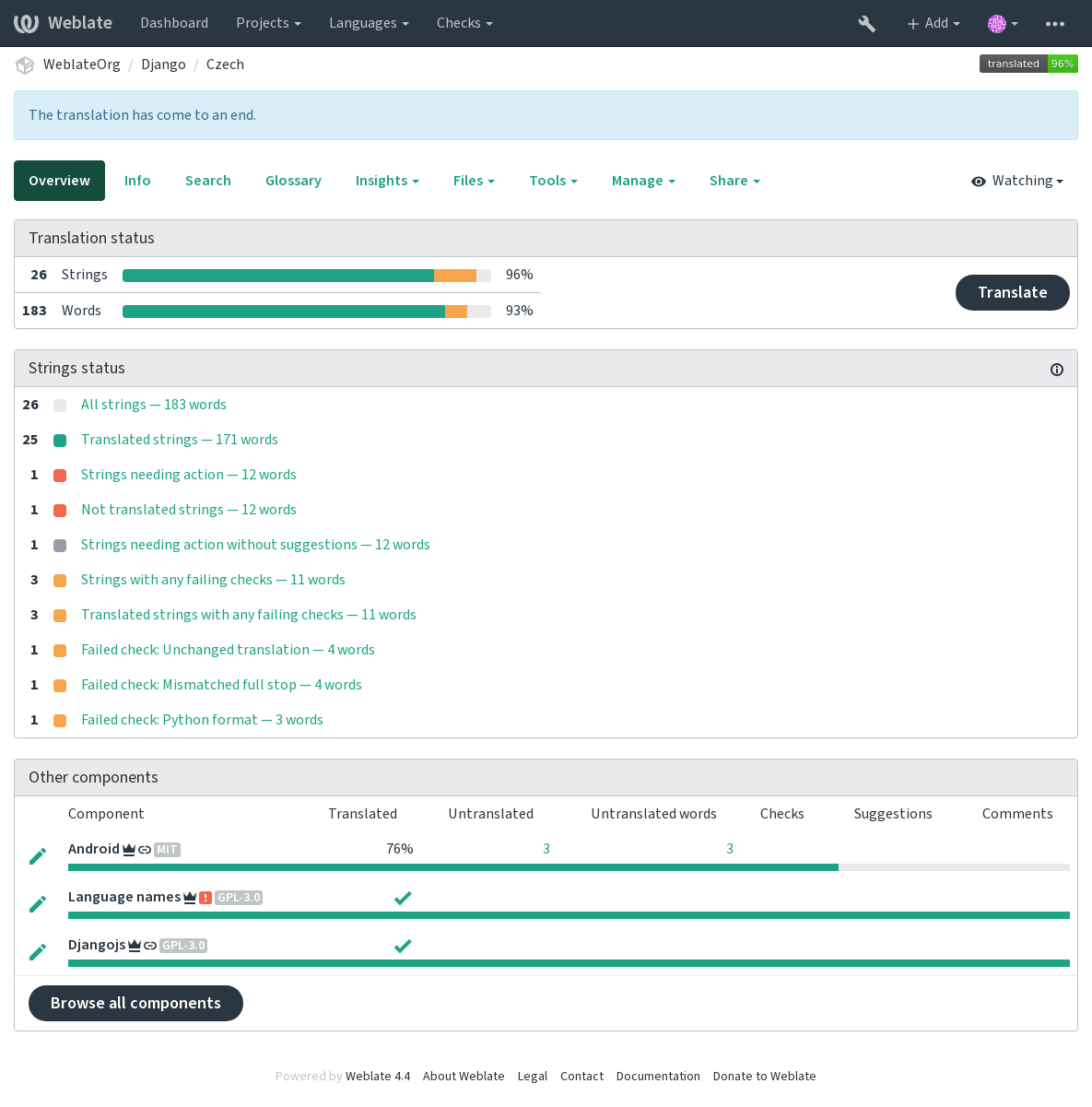
Quando enviar uma tradução com uma verificação a falhar será imediatamente mostrada ao utilizador:
Correções automáticas¶
Além de Verificações de qualidade, o Weblate pode corrigir automaticamente alguns erros comuns em cadeias traduzidas. Use-o com cuidado para não causar erros por meio disto.
Veja também
Verificações de qualidade¶
O Weblate emprega uma ampla gama de verificações de qualidade em cadeias. A secção a seguir descreve todos eles em mais detalhe. Há também verificações específicas de idiomas. Por favor, preencha um relatório de erro se alguma verificação for relatada por engano.
Veja também
Verificações de tradução¶
Executado a cada alteração da tradução, ajuda os tradutores a manter traduções de boa qualidade.
Markup BBcode¶
BBcode na tradução não corresponde à fonte
BBCode representa marcação simples, como, por exemplo, destacar partes importantes de uma mensagem em fonte em negrito ou itálico.
Esta verificação garante que eles também estejam na tradução.
Nota
O método para detetar BBcode é atualmente bastante simples, então esta verificação pode produzir falsos positivos.
Palavras consecutivas duplicadas¶
O texto contém a mesma palavra duas vezes de seguida:
Novo na versão 4.1.
Verifica se não há palavras duplicadas consecutivas numa tradução. Isso geralmente indica um erro na tradução.
Dica
Esta verificação inclui regras específicas do idioma para evitar falsos positivos. Caso seja falso no seu caso, avise-nos. Veja Reporting issues in Weblate.
Espaço duplo¶
A tradução contém espaços duplos
Verifica se espaços duplos estão presentes na tradução para evitar falsos positivos em outras verificações relacionadas ao espaço.
A verificação é falsa quando espaços duplos são encontrados na fonte, o que significa que os espaços duplos são intencionais.
Cadeias formatadas¶
Verifica se a formatação em cadeias é replicada entre a fonte e a tradução. Omitir cadeias de formato na tradução geralmente causa problemas graves, de modo que a formatação em cadeias geralmente deve coincidir com a fonte.
O Weblate tem suporte a verificar cadeias de formato em vários idiomas. A verificação não é ativada automaticamente, somente se uma cadeia for sinalizada adequadamente (por exemplo, «c-format” para formato C). O Gettext adiciona-o automaticamente, mas provavelmente terá que adicioná-lo manualmente para outros formatos de ficheiro ou se os seus ficheiros PO não forem gerados por xgettext.
Isso pode ser feito por unidade (ver Additional info on source strings) na Component configuration. Tê-lo definido por componente é mais simples, mas pode levar a falsos positivos no caso de a cadeia não ser interpretada como uma cadeia de formatação, mas a sintaxe de textos de formato passa a ser usada.
Dica
Caso a verificação de formato específico não esteja disponível no Weblate, pode usar Espaços reservados genéricos.
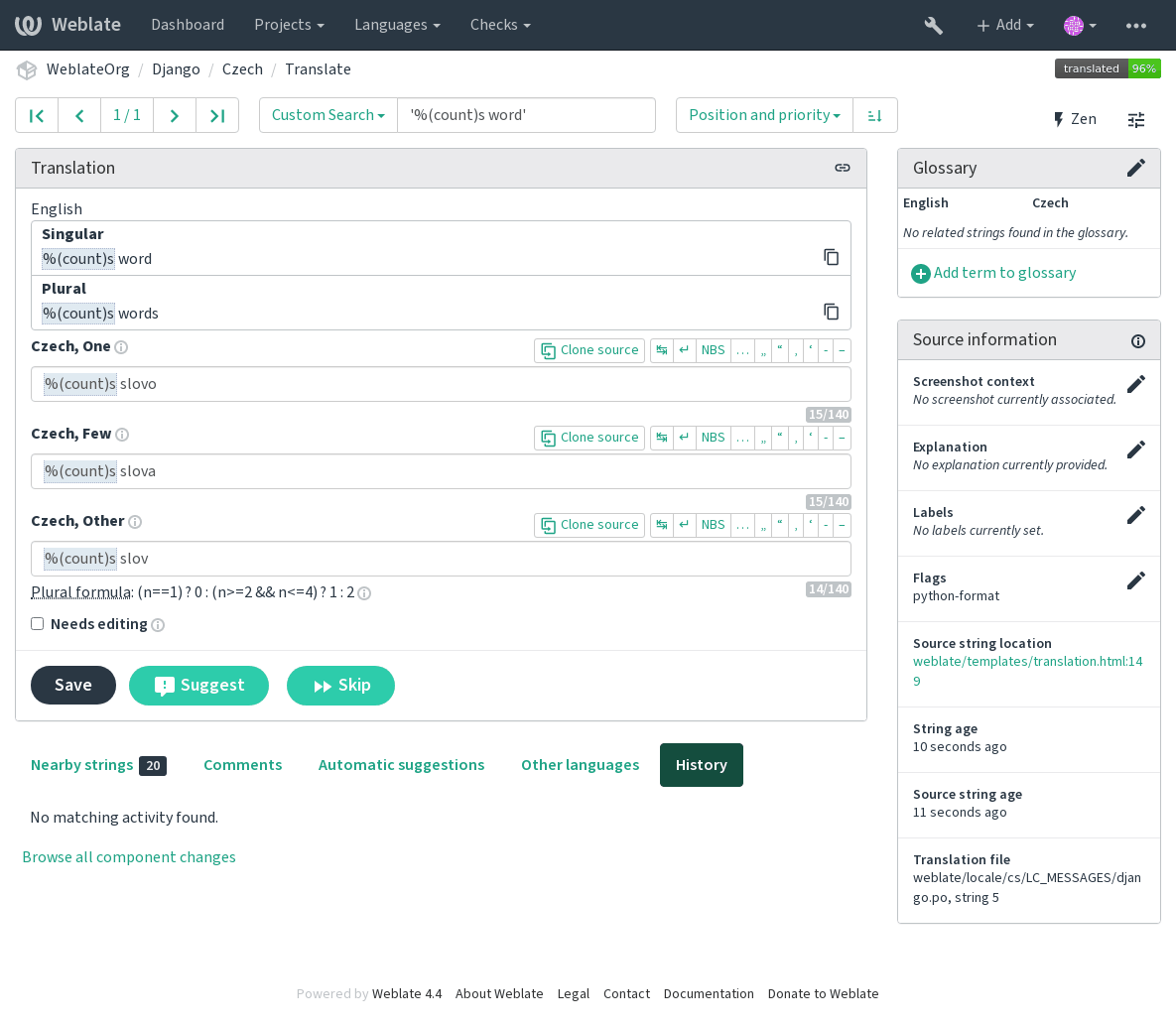
Além de verificar, isso também destacará as cadeias de formatação para inseri-los facilmente em cadeias traduzidas:
Cadeia de interpolação AngularJS¶
A cadeia de interpolação AngularJS não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato nomeado |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
angularjs-format |
Veja também
Formato C¶
A cadeia de formato C não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
c-format |
Veja também
Formato C#¶
A cadeia de formato C# não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
c-sharp-format |
Veja também
Literais de modelo de ECMAScript¶
Os literais de modelo de ECMAScript não correspondem à fonte
Interpolação |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
es-format |
Veja também
Interpolação de i18next¶
A interpolação de i18next não corresponde à fonte
Novo na versão 4.0.
Interpolação |
|
Aninhamento |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
i18next-interpolation |
Veja também
Formato Java¶
A cadeia de formato Java não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
java-format |
Veja também
Formato de Mensagem Java¶
A cadeia de MessageFormat de Java não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
java-messageformat ativa a verificação incondicionalmente |
auto-java-messageformat ativa a verificação somente se houver uma cadeia de formato na fonte |
Veja também
Formato JavaScript¶
A cadeia de formato JavaScript não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
javascript-format |
Veja também
Espaços reservados de percentagem¶
Os espaços reservados de percentagem não correspondem à fonte
Novo na versão 4.0.
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
percent-placeholders |
Formato Perl¶
A cadeia de formato Perl não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
perl-format |
Veja também
Formato PHP¶
A cadeia de formato PHP não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
php-format |
Veja também
Formato de chaveta Python¶
A cadeia de formato de chaves Python não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato nomeado |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
python-brace-format |
Veja também
Formato Python¶
A cadeia de formato Python não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato nomeado |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
python-format |
Veja também
Formato Qt¶
A cadeia de formato Qt não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
qt-format |
Veja também
Forma plural Qt¶
A cadeia de formato de plural do Qt não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato de plural |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
qt-plural-format |
Veja também
Formato Ruby¶
A cadeia de formato Ruby não corresponde à fonte
Cadeia de formato simples |
|
Cadeia de formato de posição |
|
Cadeia de formato nomeado |
|
Cadeia de modelo nomeado |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
ruby-format |
Veja também
Formatação vue I18n¶
A formatação Vue I18n não corresponde com a fonte
Formatação nomeada |
|
Formatação i18n de Rails |
|
Mensagens de localidade vinculadas |
|
Sinalize para ativar |
vue-format |
Veja também
Foi traduzido¶
Esta cadeia foi traduzida no passado
Significa que uma cadeia já foi traduzida. Isso pode acontecer quando as traduções foram revertidas no VCS ou perdidas de outra forma.
Inconsistente¶
Esta cadeia tem mais que uma tradução neste projeto ou não é traduzida em alguns componentes.
O Weblate verifica traduções da mesma cadeia em todas as traduções de um projeto para ajudar a manter traduções consistentes.
A verificação falha em traduções diferentes de uma cadeia dentro de um projeto. Isso também pode levar a inconsistências nas verificações exibidas. Pode encontrar outras traduções desta cadeia na guia Outras ocorrências.
Nota
Esta verificação também é disparada no caso de a cadeia estar traduzida num componente e não em outro. Ela pode ser usada como uma maneira rápida de manusear manualmente cadeias que não estão traduzidas em alguns componentes apenas clicando no botão Usar esta tradução exibido em cada linha na guia Outras ocorrências.
Pode usar Tradução automática para automatizar a tradução de cadeias recém-adicionadas que já são traduzidas em outro componente.
Veja também
Letra Kashida utilizada¶
As letras kashida decorativas não devem ser usadas
Novo na versão 3.5.
As letras Kashida decorativas não devem ser usadas na tradução. Estas também são conhecidas como Tatweel.
Veja também
Hiperligações de marcação¶
Markdown links do not match source
Novo na versão 3.5.
Markdown links do not match source.
Veja também
Referências de Markdown¶
Markdown link references do not match source
Novo na versão 3.5.
Markdown link references do not match source.
Veja também
Sintaxe de Markdown¶
Markdown syntax does not match source
Novo na versão 3.5.
A sintaxe de Markdown não coincide com a fonte
Veja também
Tamanho máximo da tradução¶
Translation should not exceed given length
Checks that translations are of acceptable length to fit available space. This only checks for the length of translation characters.
Unlike the other checks, the flag should be set as a key:value pair like
max-length:100.
Dica
This check looks at number of chars, what might not be the best metric when using proportional fonts to render the text. The Tamanho máximo da tradução check does check actual rendering of the text.
The replacements: flag might be also useful to expand placeables before
checking the string.
Tamanho máximo da tradução¶
Translation rendered text should not exceed given size
Novo na versão 3.7.
Translation rendered text should not exceed given size. It renders the text with line wrapping and checks if it fits into given boundaries.
This check needs one or two parameters - maximal width and maximal number of lines. In case the number of lines is not provided, one line text is considered.
You can also configure used font by font-* directives (see
Personalizar o comportamento), for example following translation flags say that the
text rendered with ubuntu font size 22 should fit into two lines and 500
pixels:
max-size:500:2, font-family:ubuntu, font-size:22
Dica
You might want to set font-* directives in Component configuration to have the same
font configured for all strings within a component. You can override those
values per string in case you need to customize it per string.
The replacements: flag might be also useful to expand placeables before
checking the string.
\n não correspondente¶
Quantidade de \n na tradução não corresponde à da fonte
Usually escaped newlines are important for formatting program output.
Check fails if the number of \n literals in translation do not match the source.
Dois pontos não correspondentes¶
Source and translation do not both end with a colon
Checks that colons are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of colons is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese or Japanese).
Veja também
Reticências não correspondentes¶
Source and translation do not both end with an ellipsis
Checks that trailing ellipses are replicated between both source and translation.
This only checks for real ellipsis (…) not for three dots (...).
An ellipsis is usually rendered nicer than three dots in print, and sounds better with text-to-speech.
Veja também
Ponto de exclamação não correspondente¶
Source and translation do not both end with an exclamation mark
Checks that exclamations are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of exclamation marks is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Armenian, Limbu, Myanmar or Nko).
Veja também
Ponto final não correspondente¶
Source and translation do not both end with a full stop
Checks that full stops are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of full stops is checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese, Japanese, Devanagari or Urdu).
Veja também
Ponto de interrogação não correspondente¶
A fonte e a tradução não terminam ambas com um ponto de interrogação
Checks that question marks are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of question marks is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Armenian, Arabic, Chinese, Korean, Japanese, Ethiopic, Vai or Coptic).
Veja também
Ponto e vírgula não correspondente¶
Source and translation do not both end with a semicolon
Checks that semicolons at the end of sentences are replicated between both source and translation. This can be useful to keep formatting of entries such as desktop files.
Veja também
Quebras de linha não coincidentes¶
Number of new lines in translation does not match source
Usually newlines are important for formatting program output.
Check fails if the number of \n literals in translation do not match the source.
Faltam plurais¶
Some plural forms are not translated
Checks that all plural forms of a source string have been translated. Specifics on how each plural form is used can be found in the string definition.
Failing to fill in plural forms will in some cases lead to displaying nothing when the plural form is in use.
Espaços reservados¶
Translation is missing some placeholders:
Novo na versão 3.9.
Alterado na versão 4.3: Pode usar expressões regulares como espaço reservado.
Translation is missing some placeholders. These are either extracted from the
translation file or defined manually using placeholders flag, more can be
separated with colon, strings with space can be quoted:
placeholders:$URL$:$TARGET$:"some long text"
In case you have some syntax for placeholders, you can use an regular expression:
placeholders:r"%[^% ]%"
Veja também
Espaçamento da pontuação¶
Missing non breakable space before double punctuation sign
Novo na versão 3.9.
Checks that there is non breakable space before double punctuation sign (exclamation mark, question mark, semicolon and colon). This rule is used only in a few selected languages like French or Breton, where space before double punctuation sign is a typographic rule.
Veja também
Expressão regular¶
Translation does not match regular expression:
Novo na versão 3.9.
Translation does not match regular expression. The expression is either extracted from the
translation file or defined manually using regex flag:
regex:^foo|bar$
Mesmos plurais¶
Some plural forms are translated in the same way
Check that fails if some plural forms are duplicated in the translation. In most languages they have to be different.
Nova linha no início¶
Source and translation do not both start with a newline
Newlines usually appear in source strings for good reason, omissions or additions can lead to formatting problems when the translated text is put to use.
Veja também
Espaços no início¶
Source and translation do not both start with same number of spaces
A space in the beginning of a string is usually used for indentation in the interface and thus important to keep.
Nova linha no final¶
Source and translation do not both end with a newline
Newlines usually appear in source strings for good reason, omissions or additions can lead to formatting problems when the translated text is put to use.
Veja também
Espaço no final¶
Source and translation do not both end with a space
Checks that trailing spaces are replicated between both source and translation.
Trailing space is usually utilized to space out neighbouring elements, so removing it might break layout.
Tradução inalterada¶
Source and translation are identical
Happens if the source and corresponding translation strings is identical, down to at least one of the plural forms. Some strings commonly found across all languages are ignored, and various markup is stripped. This reduces the number of false positives.
This check can help find strings mistakenly untranslated.
The default behavior of this check is to exclude words from the built-in
blacklist from the checking. These are words which are frequently not being
translated. This is useful to avoid false positives on short strings, which
consist only of single word which is same in several languages. This blacklist
can be disabled by adding strict-same flag to string or component.
Veja também
HTML inseguro¶
The translation uses unsafe HTML markup
Novo na versão 3.9.
The translation uses unsafe HTML markup. This check has to be enabled using
safe-html flag (see Personalizar o comportamento). There is also accompanied
autofixer which can automatically sanitize the markup.
Veja também
The HTML check is performed by the Bleach library developed by Mozilla.
URL¶
The translation does not contain an URL
Novo na versão 3.5.
The translation does not contain an URL. This is triggered only in case the unit is marked as containing URL. In that case the translation has to be a valid URL.
Markup XML¶
XML tags in translation do not match source
This usually means the resulting output will look different. In most cases this is not a desired result from changing the translation, but occasionally it is.
Checks that XML tags are replicated between both source and translation.
Espaçamento nulo¶
Translation contains extra zero-width space character
Zero-width space (<U+200B>) characters are used to break messages within words (word wrapping).
As they are usually inserted by mistake, this check is triggered once they are present in translation. Some programs might have problems when this character is used.
Veja também
Source checks¶
Source checks can help developers improve the quality of source strings.
Reticências¶
The string uses three dots (…) instead of an ellipsis character (…)
This fails when the string uses three dots (...) when it should use an ellipsis character (…).
Using the Unicode character is in most cases the better approach and looks better rendered, and may sound better with text-to-speech.
Veja também
Não traduzido há muito tempo¶
The string has not been translated for a long time
Novo na versão 4.1.
When the string has not been translated for a long time, it is can indicate problem in a source string making it hard to translate.
Várias verificações falhadas¶
The translations in several languages have failing checks
Numerous translations of this string have failing quality checks. This is usually an indication that something could be done to improve the source string.
This check failing can quite often be caused by a missing full stop at the end of a sentence, or similar minor issues which translators tend to fix in translation, while it would be better to fix it in the source string.
Várias variáveis sem nome¶
There are multiple unnamed variables in the string, making it impossible for translators to reorder them
Novo na versão 4.1.
There are multiple unnamed variables in the string, making it impossible for translators to reorder them.
Consider using named variables instead to allow translators to reorder them.
Não pluralizado¶
The string is used as plural, but not using plural forms
The string is used as a plural, but does not use plural forms. In case your translation system supports this, you should use the plural aware variant of it.
For example with Gettext in Python it could be:
from gettext import ngettext
print ngettext("Selected %d file", "Selected %d files", files) % files