Proiecte de traducere¶
Translation organization¶
Weblate organizes translatable VCS content of project/components into a tree-like structure.
The bottom level object is Project configuration, which should hold all translations belonging together (for example translation of an application in several versions and/or accompanying documentation).
On the level above, Component configuration, which is actually the component to translate, you define the VCS repository to use, and the mask of files to translate.
Above Component configuration there are individual translations, handled automatically by Weblate as translation files (which match File mask defined in Component configuration) appear in the VCS repository.
Weblate supports a wide range of translation formats (both bilingual and monolingual ones) supported by Translate Toolkit, see Supported file formats.
Notă
You can share cloned VCS repositories using Weblate internal URLs. Using this feature is highly recommended when you have many components sharing the same VCS. It improves performance and decreases required disk space.
Adding translation projects and components¶
Schimbat în versiunea 3.2: An interface for adding projects and components is included, and you no longer have to use Interfața de administrare Django.
Schimbat în versiunea 3.4: The process of adding components is now multi staged, with automated discovery of most parameters.
Based on your permissions, new translation projects and components can be created. It is always permitted for users with the Add new projects permission, and if your instance uses billing (e.g. like https://hosted.weblate.org/ see Facturare), you can also create those based on your plans allowance from the user account that manages billing.
You can view your current billing plan on a separate page:
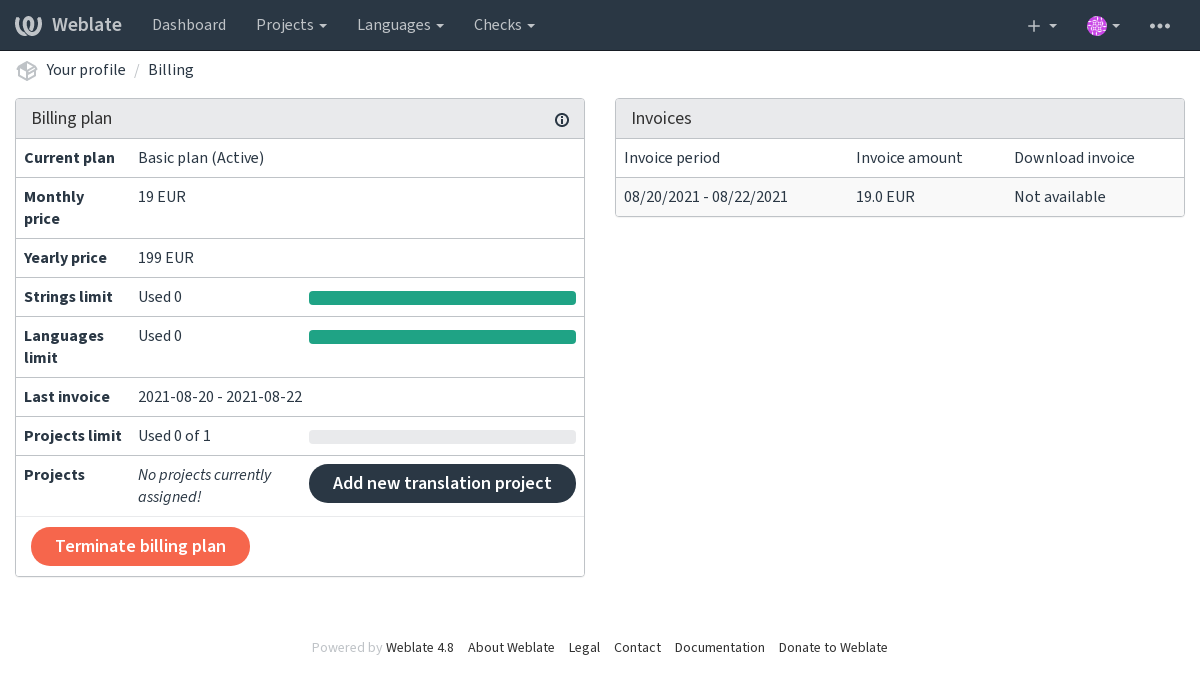
The project creation can be initiated from there, or using the menu in the navigation bar, filling in basic info about the translation project to complete addition of it:
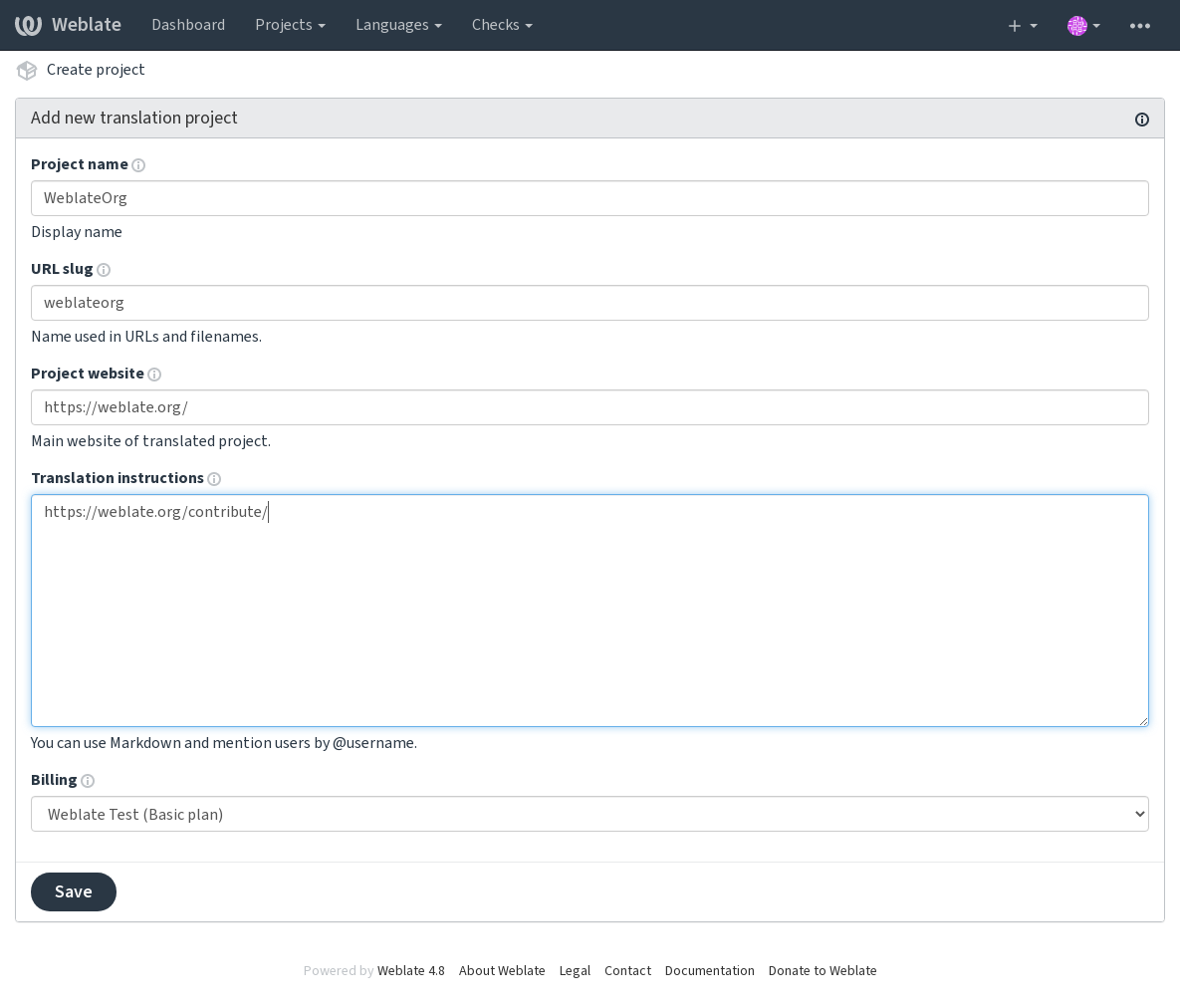
After creating the project, you are taken directly to the project page:
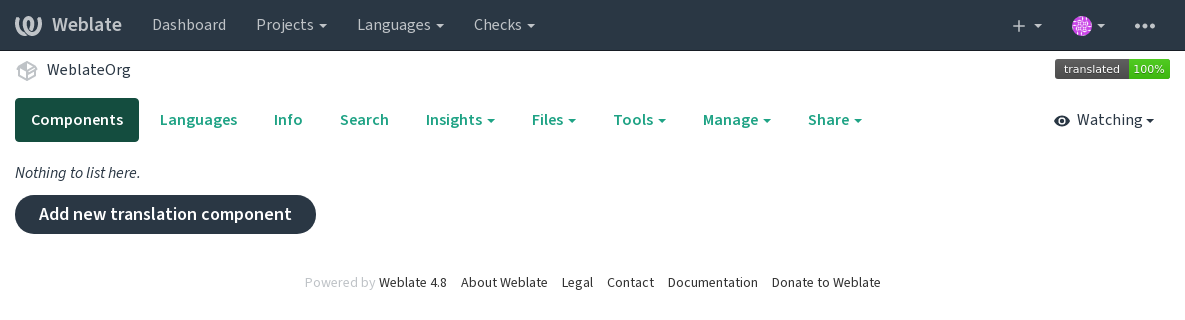
Creating a new translation component can be initiated via a single click there. The process of creating a component is multi-staged and automatically detects most translation parameters. There are several approaches to creating component:
- Din controlul versiunilor
Creates component from remote version control repository.
- Din componenta existentă
Creates additional component to existing one by choosing different files.
- Sucursală suplimentară
Creates additional component to existing one, just for different branch.
- Încărcați fișiere de traducere
Upload translation files to Weblate in case you do not have version control or do not want to integrate it with Weblate. You can later update the content using the web interface or Weblate’s REST API.
- Traduceți documentul
Upload single document or translation file and translate that.
- Începeți de la zero
Create blank translation project and add strings manually.
Once you have existing translation components, you can also easily add new ones for additional files or branches using same repository.
First you need to fill in name and repository location:
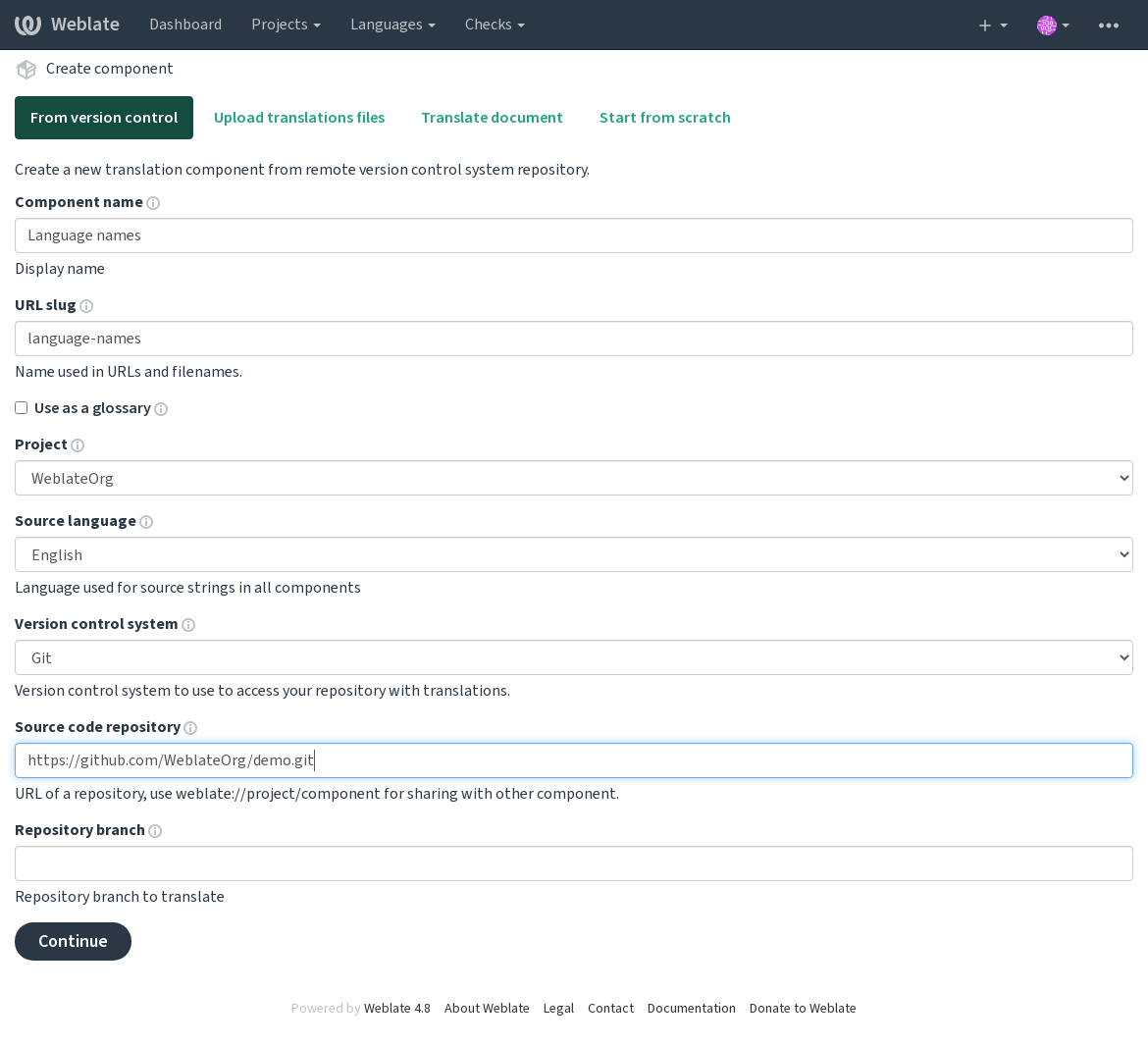
On the next page, you are presented with a list of discovered translatable resources:
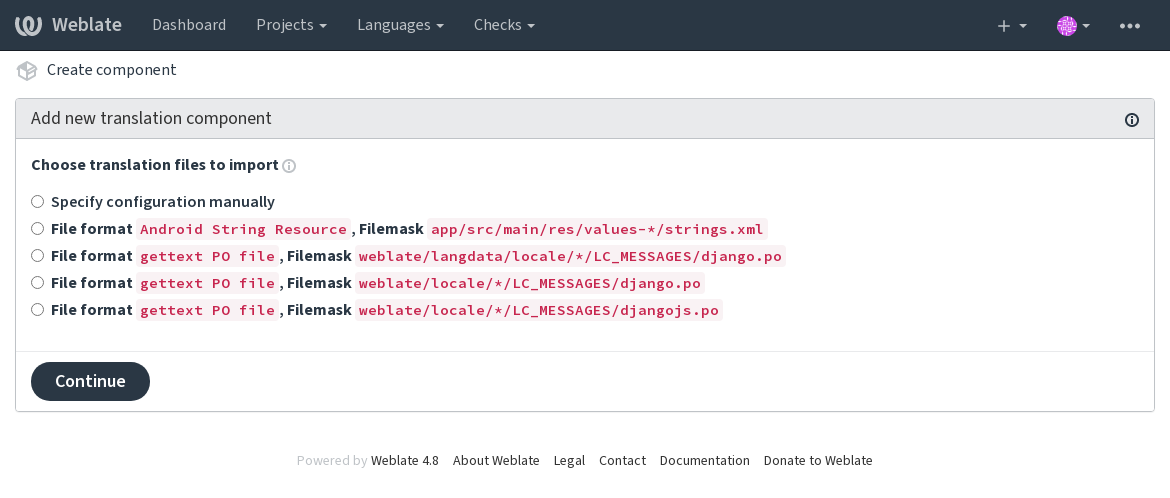
As a last step, you review the translation component info and fill in optional details:
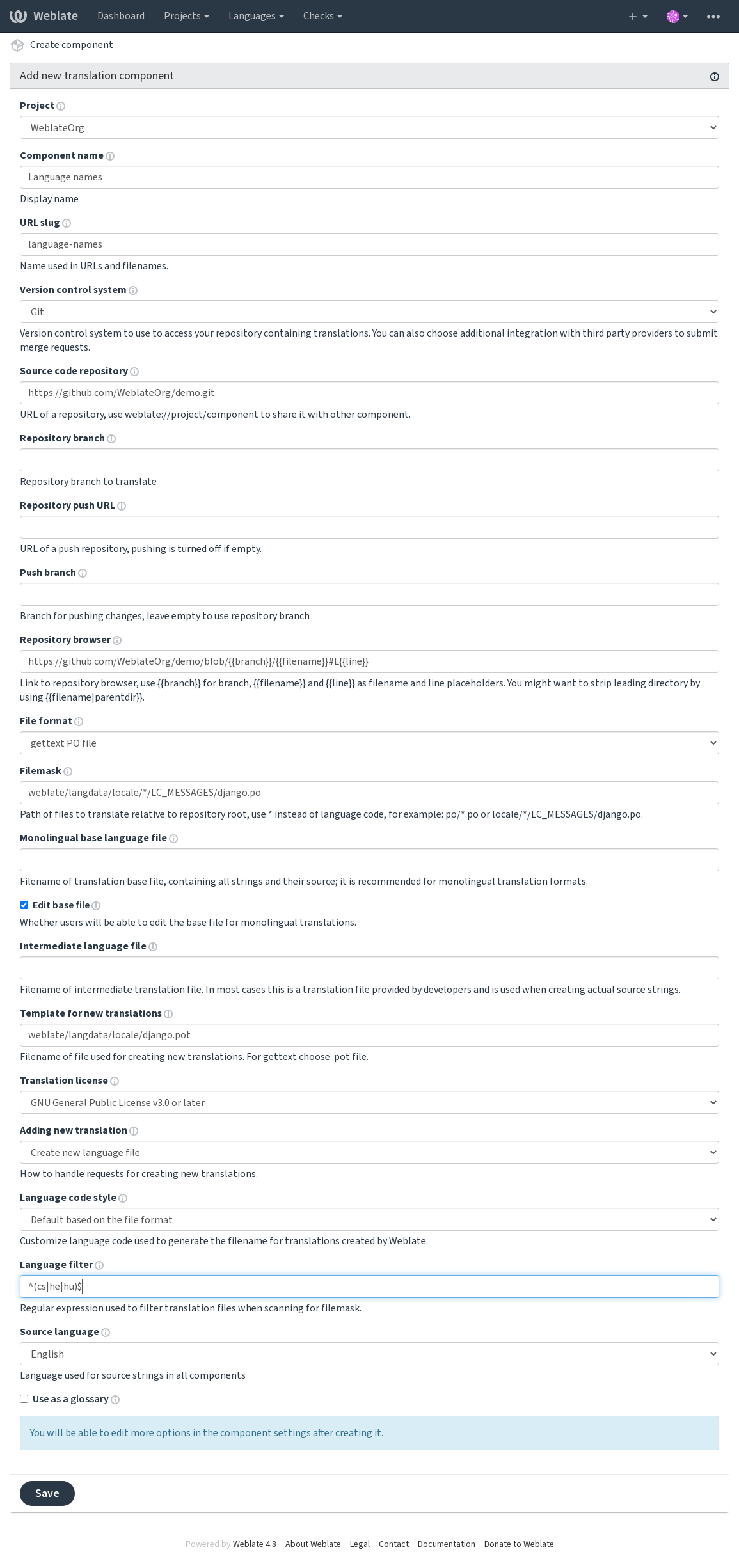
Project configuration¶
Create a translation project and then add a new component for translation in it. The project is like a shelf, in which real translations are stacked. All components in the same project share suggestions and their dictionary; the translations are also automatically propagated through all components in a single project (unless turned off in the component configuration), see Memorie de traducere.
Vezi și
These basic attributes set up and inform translators of a project:
Denumire proiect¶
Verbose project name, used to display the project name.
URL slug¶
Project name suitable for URLs.
Website-ul proiectului¶
URL where translators can find more info about the project.
This is a required parameter unless turned off by WEBSITE_REQUIRED.
Instrucțiuni de traducere¶
URL to more site with more detailed instructions for translators.
Setați antetul „Language-Team”¶
Whether Weblate should manage the Language-Team header (this is a
GNU gettext only feature right now).
Controlul accesului¶
Configure per project access control, see Control acces proiect for more details.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_ACCESS_CONTROL.
Activați recenzii¶
Enable review workflow for translations, see Dedicated reviewers.
Activați revizuirile sursei¶
Enable review workflow for source strings, see Source strings reviews.
Activați cârligele¶
Whether unauthenticated Cârlige de notificare are to be used for this repository.
Aliasuri lingvistice¶
Define language codes mapping when importing translations into Weblate. Use this when language codes are inconsistent in your repositories and you want to get a consistent view in Weblate or in case you want to use non-standard naming of your translation files.
The typical use case might be mapping American English to English: en_US:en
Multiple mappings to be separated by comma: en_GB:en,en_US:en
Using non standard code: ia_FOO:ia
Sugestie
The language codes are mapped when matching the translation files and the matches are case sensitive, so make sure you use the source language codes in same form as used in the filenames.
Vezi și
Component configuration¶
A component is a grouping of something for translation. You enter a VCS repository location and file mask for which files you want translated, and Weblate automatically fetches from this VCS, and finds all matching translatable files.
Vezi și
You can find some examples of typical configurations in the Supported file formats.
Notă
It is recommended to keep translation components to a reasonable size - split the translation by anything that makes sense in your case (individual apps or addons, book chapters or websites).
Weblate easily handles translations with 10000s of strings, but it is harder to split work and coordinate among translators with such large translation components.
Should the language definition for a translation be missing, an empty definition is created and named as „cs_CZ (generated)”. You should adjust the definition and report this back to the Weblate authors, so that the missing languages can be included in next release.
The component contains all important parameters for working with the VCS, and for getting translations out of it:
Denumirea componentei¶
Verbose component name, used to display the component name.
Component slug¶
Component name suitable for URLs.
Component project¶
Project configuration where the component belongs.
Sistem de control al versiunilor¶
VCS to use, see Integrarea controlului versiunilor for details.
Vezi și
Depozitul de cod sursă¶
VCS repository used to pull changes.
Vezi și
See Accessing repositories for more details on specifying URLs.
Sugestie
This can either be a real VCS URL or weblate://project/component
indicating that the repository should be shared with another component.
See Weblate internal URLs for more details.
URL de împingere a depozitului¶
Repository URL used for pushing. This setting is used only for Git and Mercurial and push support is turned off for these when this is empty.
Vezi și
See Accessing repositories for more details on how to specify a repository URL and Pushing changes from Weblate for more details on pushing changes from Weblate.
Navigator de depozite¶
URL of repository browser used to display source files (location of used messages). When empty, no such links will be generated. You can use Template markup.
For example on GitHub, use something like:
https://github.com/WeblateOrg/hello/blob/{{branch}}/{{filename}}#L{{line}}
In case your paths are relative to different folder (path contains ..), you
might want to strip leading directory by parentdir filter (see
Template markup):
https://github.com/WeblateOrg/hello/blob/{{branch}}/{{filename|parentdir}}#L{{line}}
URL-ul depozitului exportat¶
URL where changes made by Weblate are exported. This is important when Traducere continuă is not used, or when there is a need to manually merge changes. You can use Git exporter to automate this for Git repositories.
Ramura de depozit¶
Which branch to checkout from the VCS, and where to look for translations.
Împingeți ramura¶
Branch for pushing changes, leave empty to use Ramura de depozit.
Notă
This is currently only supported for Git, GitLab and GitHub, it is ignored for other VCS integrations.
Vezi și
File mask¶
Mask of files to translate, including path. It should include one „*” replacing language code (see Language definitions for info on how this is processed). In case your repository contains more than one translation file (e.g. more gettext domains), you need to create a component for each of them.
For example po/*.po or locale/*/LC_MESSAGES/django.po.
In case your filename contains special characters such as [, ], these need
to be escaped as [[] or []].
Fișier de limbă de bază monolingvă¶
Base file containing string definitions for Componente monolingve.
Editarea fișierului de bază¶
Whether to allow editing the base file for Componente monolingve.
Fișier de limbaj intermediar¶
Intermediate language file for Componente monolingve. In most cases this is a translation file provided by developers and is used when creating actual source strings.
When set, the source strings are based on this file, but all other languages are based on Fișier de limbă de bază monolingvă. In case the string is not translated into the source langugage, translating to other languages is prohibited. This provides Quality gateway for the source strings.
Șablon pentru traduceri noi¶
Base file used to generate new translations, e.g. .pot file with gettext.
Sugestie
In many monolingual formats Weblate starts with blank file by default. Use this in case you want to have all strings present with empty value when creating new translation.
Formatul fișierului¶
Translation file format, see also Supported file formats.
Adresa de raportare a erorilor din șirul sursă¶
Email address used for reporting upstream bugs. This address will also receive notification about any source string comments made in Weblate.
Permiteți propagarea traducerii¶
You can turn off propagation of translations to this component from other components within same project. This really depends on what you are translating, sometimes it’s desirable to have make use of a translation more than once.
It’s usually a good idea to turn this off for monolingual translations, unless you are using the same IDs across the whole project.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_TRANSLATION_PROPAGATION.
Enable suggestions¶
Whether translation suggestions are accepted for this component.
Votul prin sugestie¶
Turns on vote casting for suggestions, see Votul prin sugestie.
Sugestii de autoacceptare¶
Automatically accept voted suggestions, see Votul prin sugestie.
Steaguri de traducere¶
Customization of quality checks and other Weblate behavior, see Personalizarea comportamentului cu ajutorul stegulețelor.
Controale forțate¶
List of checks which can not be ignored, see Executarea controalelor.
Notă
Enforcing the check does not automatically enable it, you still should enabled it using Personalizarea comportamentului cu ajutorul stegulețelor in Steaguri de traducere or Additional info on source strings.
Licență de traducere¶
License of the translation (does not need to be the same as the source code license).
Acord de colaborare¶
Acordul de utilizare care trebuie aprobat înainte ca un utilizator să poată traduce această componentă.
Adăugarea unei noi traduceri¶
How to handle requests for creation of new languages. Available options:
- Contactează întreținătorii
User can select desired language and the project maintainers will receive a notification about this. It is up to them to add (or not) the language to the repository.
- Indicați instrucțiunile de traducere URL
User is presented a link to page which describes process of starting new translations. Use this in case more formal process is desired (for example forming a team of people before starting actual translation).
- Crearea unui nou fișier de limbă
User can select language and Weblate automatically creates the file for it and translation can begin.
- Dezactivați adăugarea de noi traduceri
There will be no option for user to start new translation.
Sugestie
The project admins can add new translations even if it is disabled here when it is possible (either Șablon pentru traduceri noi or the file format supports starting from an empty file).
Gestionați șirurile de caractere¶
Nou în versiunea 4.5.
Configures whether users in Weblate will be allowed to add new strings and remove existing ones. Adjust this to match your localization workflow - how the new strings are supposed to be introduced.
For bilingual formats, the strings are typically extracted from the source code (for example by using xgettext) and adding new strings in Weblate should be disabled (they would be discarded next time you update the translation files). In Weblate you can manage strings for every translation and it does not enforce the strings in all translations to be consistent.
For monolingual formats, the strings are managed only on source language and are automatically added or removed in the translations. The strings appear in the translation files once they are translated.
Stil de cod lingvistic¶
Personalizați codul de limbă utilizat pentru a genera numele de fișier pentru traducerile create de Weblate.
Stil de fuziune¶
You can configure how updates from the upstream repository are handled. This might not be supported for some VCSs. See Merge or rebase for more details.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_MERGE_STYLE.
Commit, add, delete, merge and addon messages¶
Message used when committing a translation, see Template markup.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_ADD_MESSAGE,
DEFAULT_ADDON_MESSAGE, DEFAULT_COMMIT_MESSAGE,
DEFAULT_DELETE_MESSAGE, DEFAULT_MERGE_MESSAGE.
Împingeți pe comitere¶
Whether committed changes should be automatically pushed to the upstream repository. When enabled, the push is initiated once Weblate commits changes to its underlying repository (see Lazy commits). To actually enable pushing Repository push URL has to be configured as well.
Vârsta modificărilor care urmează să fie confirmate¶
Sets how old (in hours) changes have to be before they are committed by
background task or the commit_pending management command. All
changes in a component are committed once there is at least one change
older than this period.
Default value can be changed by COMMIT_PENDING_HOURS.
Sugestie
There are other situations where pending changes might be committed, see Lazy commits.
Blocare pe eroare¶
Locks the component (and linked components, see Weblate internal URLs) upon the first failed push or merge into its upstream repository, or pull from it. This avoids adding another conflicts, which would have to be resolved manually.
The component will be automatically unlocked once there are no repository errors left.
Limba sursă¶
Language used for source strings. Change this if you are translating from something else than English.
Sugestie
In case you are translating bilingual files from English, but want to be able to do fixes in the English translation as well, choose English (Developer) as a source language to avoid conflict between the name of the source language and the existing translation.
For monolingual translations, you can use intermediate translation in this case, see Fișier de limbaj intermediar.
Filtru lingvistic¶
Regular expression used to filter the translation when scanning for filemask. It can be used to limit the list of languages managed by Weblate.
Notă
You need to list language codes as they appear in the filename.
Some examples of filtering:
Filter description |
Expresie regulată |
|---|---|
Selected languages only |
|
Exclude languages |
|
Filter two letter codes only |
|
Exclude non language files |
|
Include all files (default) |
|
Variante expresie regulată¶
Regular expression used to determine the variants of a string, see String variants.
Notă
Most of the fields can be edited by project owners or managers, in the Weblate interface.
Prioritate¶
Componentele cu prioritate mai mare sunt oferite mai întâi traducătorilor.
Restricted access¶
By default the component is visible to anybody who has access to the project, even if the person can not perform any changes in the component. This makes it easier to keep translation consistency within the project.
Restricting access at a component, or component-list level takes over access permission to a component, regardless of project-level permissions. You will have to grant access to it explicitly. This can be done through granting access to a new user group and putting users in it, or using the default custom or private access control groups.
The default value can be changed in DEFAULT_RESTRICTED_COMPONENT.
Sugestie
This applies to project admins as well — please make sure you will not loose access to the component after toggling the status.
Utilizarea ca glosar¶
Nou în versiunea 4.5.
Allows using this component as a glossary. You can configure how it will be listed using Glosar culoare.
The glossary will be accessible in all projects defined by Cota în proiecte.
It is recommended to enable Gestionați șirurile de caractere on glossaries in order to allow adding new words to them.
Vezi și
Glosar culoare¶
Display color for a glossary used when showing word matches.
Template markup¶
Weblate uses simple markup language in several places where text rendering is needed. It is based on The Django template language, so it can be quite powerful.
Currently it is used in:
Commit message formatting, see Component configuration
There following variables are available in the component templates:
{{ language_code }}Codul limbii
{{ language_name }}Numele limbii
{{ component_name }}Denumirea componentei
{{ component_slug }}Component slug
{{ project_name }}Denumire proiect
{{ project_slug }}Project slug
{{ url }}Translation URL
{{ filename }}Numele fișierului de traducere
{{ stats }}Translation stats, this has further attributes, examples below.
{{ stats.all }}Total strings count
{{ stats.fuzzy }}Count of strings needing review
{{ stats.fuzzy_percent }}Percent of strings needing review
{{ stats.translated }}Translated strings count
{{ stats.translated_percent }}Translated strings percent
{{ stats.allchecks }}Number of strings with failing checks
{{ stats.allchecks_percent }}Percent of strings with failing checks
{{ author }}Author of current commit, available only in the commit scope.
{{ addon_name }}Name of currently executed addon, available only in the addon commit message.
The following variables are available in the repository browser or editor templates:
{{branch}}current branch
{{line}}line in file
{{filename}}filename, you can also strip leading parts using the
parentdirfilter, for example{{filename|parentdir}}
You can combine them with filters:
{{ component|title }}
You can use conditions:
{% if stats.translated_percent > 80 %}Well translated!{% endif %}
There is additional tag available for replacing characters:
{% replace component "-" " " %}
You can combine it with filters:
{% replace component|capfirst "-" " " %}
There are also additional filter to manipulate with filenames:
Directory of a file: {{ filename|dirname }}
File without extension: {{ filename|stripext }}
File in parent dir: {{ filename|parentdir }}
It can be used multiple times: {{ filename|parentdir|parentdir }}
…and other Django template features.
Importing speed¶
Fetching VCS repository and importing translations to Weblate can be a lengthy process, depending on size of your translations. Here are some tips:
Optimize configuration¶
The default configuration is useful for testing and debugging Weblate, while for a production setup, you should do some adjustments. Many of them have quite a big impact on performance. Please check Production setup for more details, especially:
Configure Celery for executing background tasks (see Background tasks using Celery)
Check resource limits¶
If you are importing huge translations or repositories, you might be hit by resource limitations of your server.
Check the amount of free memory, having translation files cached by the operating system will greatly improve performance.
Disk operations might be bottleneck if there is a lot of strings to process—the disk is pushed by both Weblate and the database.
Additional CPU cores might help improve performance of background tasks (see Background tasks using Celery).
Disable unneeded checks¶
Some quality checks can be quite expensive, and if not needed,
can save you some time during import if omitted. See CHECK_LIST for
info on configuration.
Automatic creation of components¶
In case your project has dozen of translation files (e.g. for different
gettext domains, or parts of Android apps), you might want to import them
automatically. This can either be achieved from the command line by using
import_project or import_json, or by installing the
Descoperirea componentelor addon.
To use the addon, you first need to create a component for one translation file (choose the one that is the least likely to be renamed or removed in future), and install the addon on this component.
For the management commands, you need to create a project which will contain all
components and then run import_project or
import_json.