Web サービスを連携して翻訳¶
There is infrastructure in place so that your translation closely follows development. This way translators can work on translations the entire time, instead of working through huge amount of new text just prior to release.
参考
Integrating with Weblate describes basic ways to integrate your development with Weblate.
This is the process:
Developers make changes and push them to the VCS repository.
Optionally the translation files are updated (this depends on the file format, see Why does Weblate still show old translation strings when I've updated the template?).
Weblate pulls changes from the VCS repository, see Updating repositories.
Once Weblate detects changes in translations, translators are notified based on their subscription settings.
Translators submit translations using the Weblate web interface, or upload offline changes.
Once the translators are finished, Weblate commits the changes to the local repository (see Lazy commits) and pushes them back if it has permissions to do so (see Pushing changes from Weblate).
Updating repositories¶
You should set up some way of updating backend repositories from their source.
Use 通知フック to integrate with most of common code hosting services
リポジトリ管理または :ref:'api' あるいは :ref:'wlc' を使用して手動で更新を起動させる
Enable
AUTO_UPDATEto automatically update all components on your Weblate instanceExecute
updategit(with selection of project or --all to update all)
Weblate がリポジトリを更新するたびに、更新後のアドオンが起動、参照 アドオン。
Avoiding merge conflicts¶
The merge conflicts from Weblate arise when same file was changed both in Weblate and outside it. There are two approaches to deal with that - avoid edits outside Weblate or integrate Weblate into your updating process, so that it flushes changes prior to updating the files outside Weblate.
The first approach is easy with monolingual files - you can add new strings within Weblate and leave whole editing of the files there. For bilingual files, there is usually some kind of message extraction process to generate translatable files from the source code. In some cases this can be split into two parts - one for the extraction generates template (for example gettext POT is generated using xgettext) and then further process merges it into actual translations (the gettext PO files are updated using msgmerge). You can perform the second step within Weblate and it will make sure that all pending changes are included prior to this operation.
The second approach can be achieved by using API to force Weblate to push all pending changes and lock the translation while you are doing changes on your side.
The script for doing updates can look like this:
# Lock Weblate translation
wlc lock
# Push changes from Weblate to upstream repository
wlc push
# Pull changes from upstream repository to your local copy
git pull
# Update translation files, this example is for Django
./manage.py makemessages --keep-pot -a
git commit -m 'Locale updates' -- locale
# Push changes to upstream repository
git push
# Tell Weblate to pull changes (not needed if Weblate follows your repo
# automatically)
wlc pull
# Unlock translations
wlc unlock
If you have multiple components sharing same repository, you need to lock them all separately:
wlc lock foo/bar
wlc lock foo/baz
wlc lock foo/baj
注釈
The example uses Weblate クライアント, which needs configuration (API keys) to be able to control Weblate remotely. You can also achieve this using any HTTP client instead of wlc, e.g. curl, see API.
Automatically receiving changes from GitHub¶
Weblate comes with native support for GitHub.
If you are using Hosted Weblate, the recommended approach is to install the Weblate app, that way you will get the correct setup without having to set much up. It can also be used for pushing changes back.
To receive notifications on every push to a GitHub repository, add the Weblate Webhook in the repository settings (Webhooks) as shown on the image below:
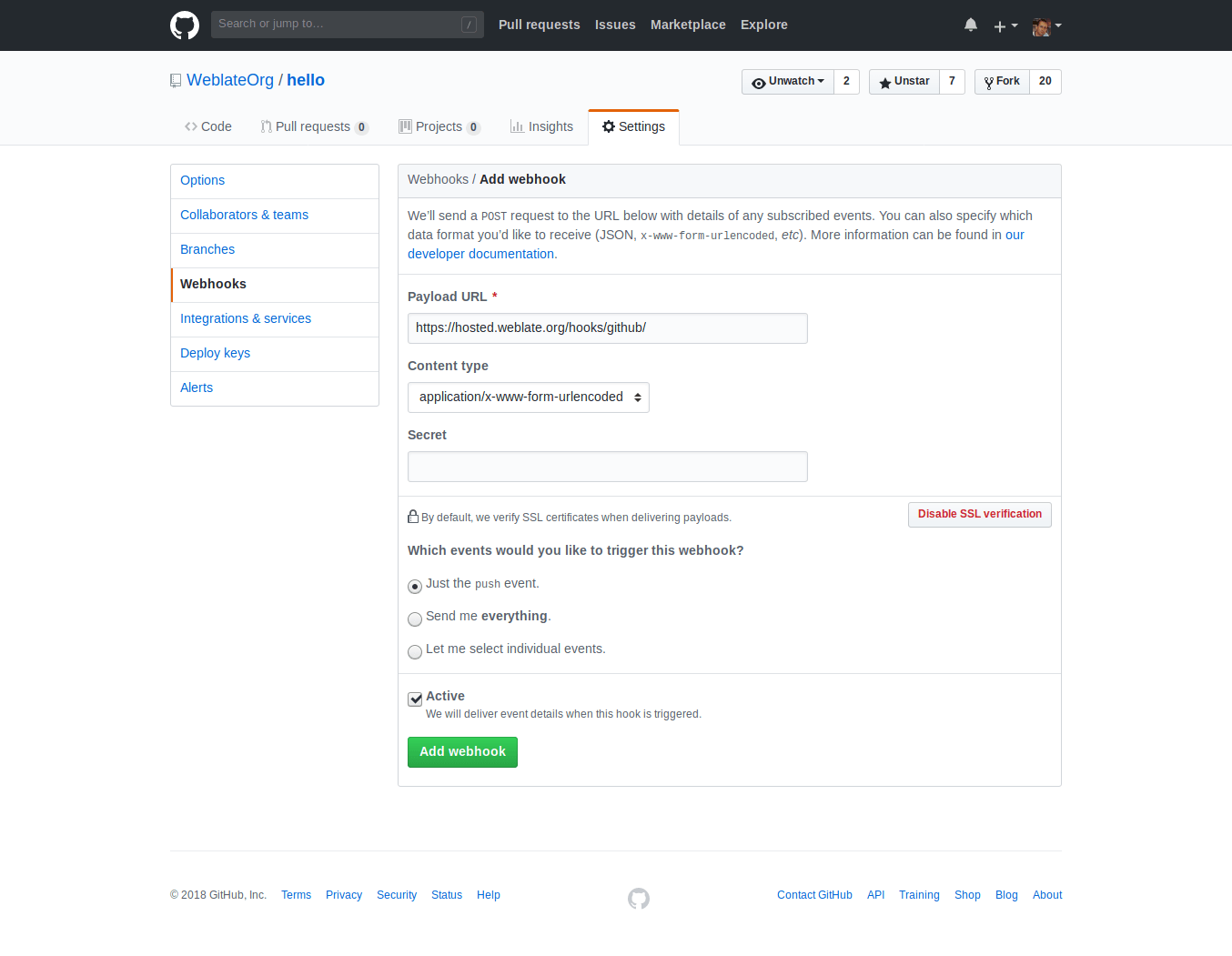
For the payload URL, append /hooks/github/ to your Weblate URL, for example
for the Hosted Weblate service, this is https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/github/.
You can leave other values at default settings (Weblate can handle both content types and consumes just the push event).
Automatically receiving changes from Bitbucket¶
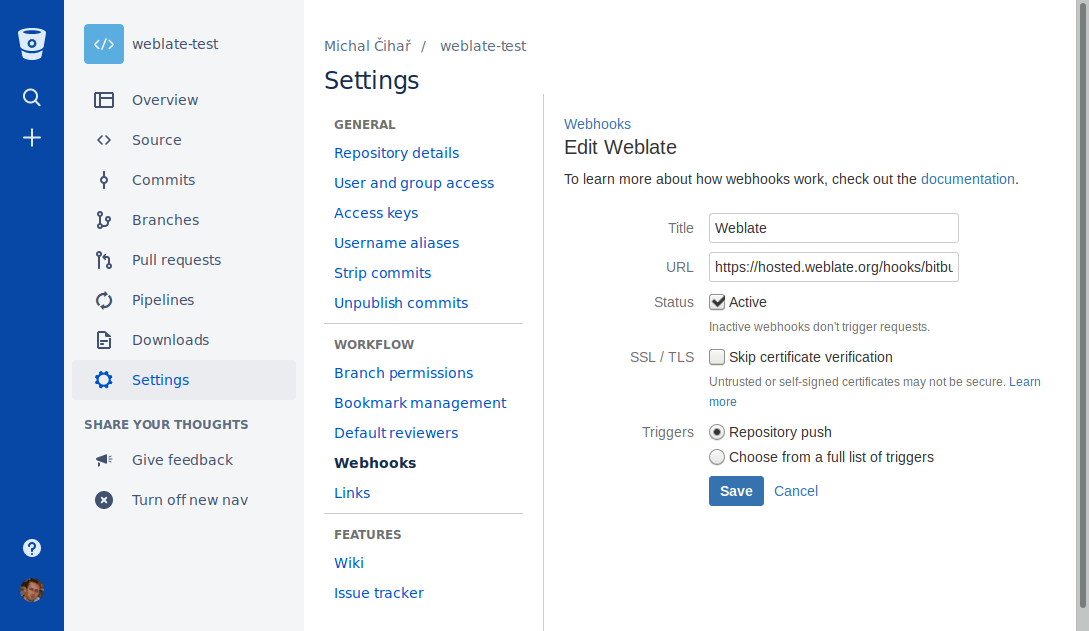
Weblate has support for Bitbucket webhooks, add a webhook
which triggers upon repository push, with destination to /hooks/bitbucket/ URL
on your Weblate installation (for example
https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/bitbucket/).
Automatically receiving changes from GitLab¶
Weblate has support for GitLab hooks, add a project webhook
with destination to /hooks/gitlab/ URL on your Weblate installation
(for example https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/gitlab/).
Pagure からの変更を自動的に受信¶
バージョン 3.3 で追加.
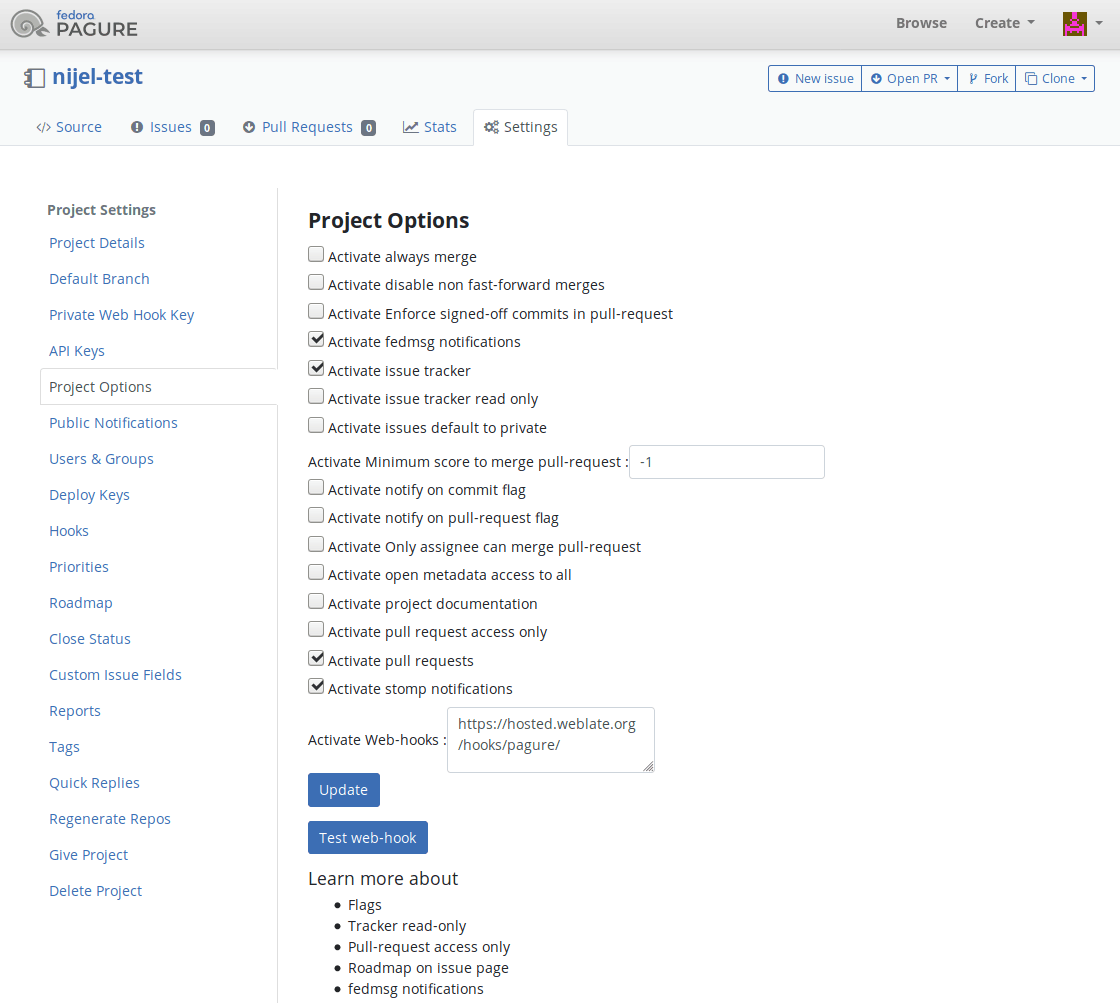
Weblate は、Pagure フックに対応しているので、あなたの Weblate のインストール上の /hooks/pagure/ URL に宛先がある WEB フックを追加します(例えば https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/pagure/)。これは、次の手順で行う Project options の中の Activate Web-hooks:
Automatically receiving changes from Azure Repos¶
バージョン 3.8 で追加.
Weblate has support for Azure Repos web hooks, add a webhook for
Code pushed event with destination to /hooks/azure/ URL on your
Weblate installation (for example https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/azure/).
This can be done in Service hooks under Project
settings.
Automatically receiving changes from Gitea Repos¶
バージョン 3.9 で追加.
Weblate has support for Gitea webhooks, add a Gitea Webhook for
Push events event with destination to /hooks/gitea/ URL on your
Weblate installation (for example https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/gitea/).
This can be done in Webhooks under repository Settings.
Automatically receiving changes from Gitee Repos¶
バージョン 3.9 で追加.
Weblate has support for Gitee webhooks, add a WebHook for
Push event with destination to /hooks/gitee/ URL on your
Weblate installation (for example https://hosted.weblate.org/hooks/gitee/).
This can be done in WebHooks under repository Management.
Automatically updating repositories nightly¶
Weblate automatically fetches remote repositories nightly to improve
performance when merging changes later. You can optionally turn this into doing
nightly merges as well, by enabling AUTO_UPDATE.
Pushing changes from Weblate¶
Each translation component can have a push URL set up (see
リポジトリの送信先 URL), and in that case Weblate will be able to push change to
the remote repository. Weblate can be also be configured to automatically push
changes on every commit (this is default, see コミット時にプッシュする).
If you do not want changes to be pushed automatically, you can do that manually
under Repository maintenance or using API via wlc push.
The push options differ based on the バージョン管理の統合 used, more details are found in that chapter.
Weblate による直接プッシュが不要な場合は、GitHub、GitLab、Pagure のプル リクエストまたは Gerrit 査読に対応しています。これを有効にするには、Component configuration で バージョン管理システム として GitHub、GitLab、Gerrit または Pagure を選択します。
Overall, following options are available with Git, GitHub and GitLab:
Desired setup |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
No push |
empty |
empty |
|
Push directly |
SSH URL |
empty |
|
別のブランチに push |
SSH URL |
Branch name |
|
GitHub pull request from fork |
empty |
empty |
|
GitHub pull request from branch |
SSH URL 1 |
Branch name |
|
GitLab merge request from fork |
empty |
empty |
|
GitLab merge request from branch |
SSH URL 1 |
Branch name |
|
フォークからの Pagure マージ リクエスト |
empty |
empty |
|
ブランチからの Pagure マージ リクエスト |
SSH URL 1 |
Branch name |
- 1(1,2,3)
Can be empty in case ソースコードのリポジトリ supports pushing.
注釈
You can also enable automatic pushing of changes after Weblate commits, this can be done in コミット時にプッシュする.
参考
See リポジトリへの接続 for setting up SSH keys, and Lazy commits for info about when Weblate decides to commit changes.
Protected branches¶
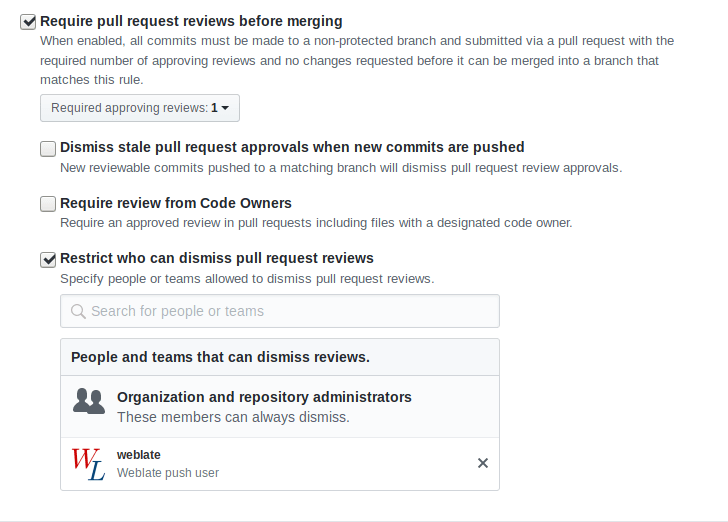
If you are using Weblate on protected branch, you can configure it to use pull requests and perform actual review on the translations (what might be problematic for languages you do not know). An alternative approach is to waive this limitation for the Weblate push user.
For example on GitHub this can be done in the repository configuration:
Merge or rebase¶
By default, Weblate merges the upstream repository into its own. This is the safest way in case you also access the underlying repository by other means. In case you don't need this, you can enable rebasing of changes on upstream, which will produce a history with fewer merge commits.
注釈
Rebasing can cause you trouble in case of complicated merges, so carefully consider whether or not you want to enable them.
Lazy commits¶
The behaviour of Weblate is to group commits from the same author into one commit if possible. This greatly reduces the number of commits, however you might need to explicitly tell it to do the commits in case you want to get the VCS repository in sync, e.g. for merge (this is by default allowed for the Managers group, see アクセス制御).
The changes in this mode are committed once any of the following conditions are fulfilled:
Somebody else changes an already changed string.
A merge from upstream occurs.
An explicit commit is requested.
Change is older than period defined as コミットするまでの経過時間 on Component configuration.
ヒント
Commits are created for every component. So in case you have many components you will still see lot of commits. You might utilize Git コミットをスカッシュ addon in that case.
If you want to commit changes more frequently and without checking of age, you can schedule a regular task to perform a commit:
CELERY_BEAT_SCHEDULE = {
# Unconditionally commit all changes every 2 minutes
"commit": {
"task": "weblate.trans.tasks.commit_pending",
# Ommiting hours will honor per component settings,
# otherwise components with no changes older than this
# won't be committed
"kwargs": {"hours": 0},
# How frequently to execute the job in seconds
"schedule": 120,
}
}
Processing repository with scripts¶
The way to customize how Weblate interacts with the repository is アドオン. Consult Executing scripts from addon for info on how to execute external scripts through addons.
Keeping translations same across components¶
Once you have multiple translation components, you might want to ensure that the same strings have same translation. This can be achieved at several levels.
Translation propagation¶
With translation propagation enabled (what is the default, see Component configuration), all new translations are automatically done in all components with matching strings. Such translations are properly credited to currently translating user in all components.
注釈
The translation propagation requires the key to be match for monolingual translation formats, so keep that in mind when creating translation keys.