Contrôles de qualité et corrections¶
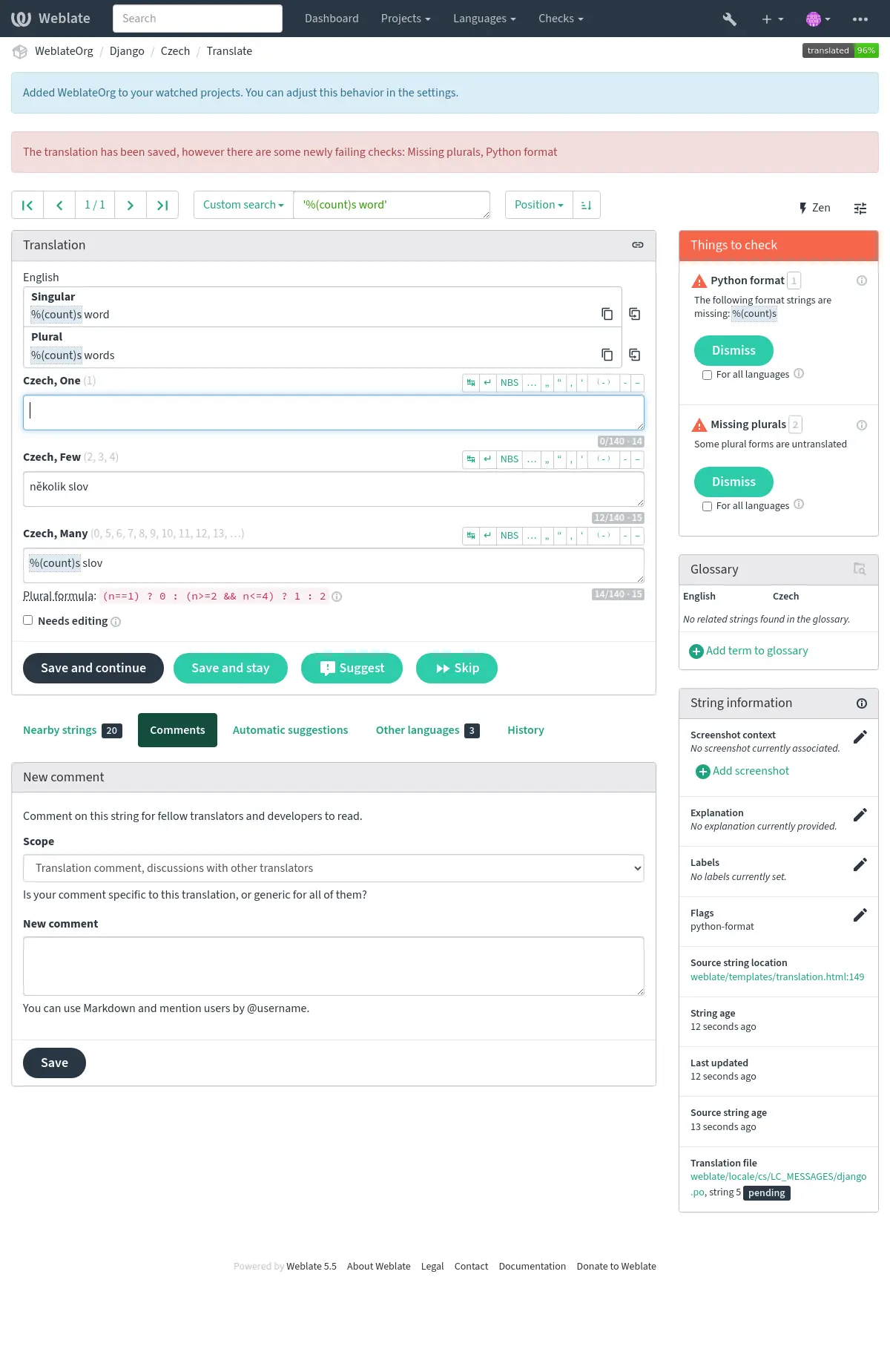
The quality checks help catch common translator errors, ensuring the translation is in good shape. The checks can be ignored in case of false positives.
Once submitting a translation with a failing check, this is immediately shown to the user:
Automatic fixups¶
In addition to Quality checks, Weblate can fix some common errors in translated strings automatically. Use it with caution to not have it add errors.
Voir aussi
Trailing ellipsis replacer¶
Replace trailing dots (...) with an ellipsis (…) to make it consistent with the source string.
Zero-width space removal¶
Zero width space is typically not desired in the translation. This fix will remove it unless it is present in the source string as well.
Control characters removal¶
Removes any control characters from the translation.
Devanagari danda¶
Replaces wrong full stop in Devanagari by Devanagari danda (।).
Espacement de ponctuation¶
Added in version 5.3.
Ensures French and Breton use correct punctuation spacing.
This fixup can be disabled via ignore-punctuation-spacing flag (which also
disables Espacement de ponctuation).
Unsafe HTML cleanup¶
When turned on using a safe-html flag it sanitizes HTML markup.
Voir aussi
Trailing and leading whitespace fixer¶
Makes leading and trailing whitespace consistent with the source string. The
behavior can be fine-tuned using ignore-begin-space and
ignore-end-space flags to skip processing parts of the string.
Quality checks¶
Weblate employs a wide range of quality checks on strings. The following section describes them all in further detail. There are also language specific checks. Please file a bug if anything is reported in error.
Voir aussi
Translation checks¶
Executed upon every translation change, helping translators maintain good quality translations.
Balisage BBCode¶
- Summary:
Les BBCodes dans la traduction ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.BBCodeCheck- Check identifier:
bbcode- Flag to ignore:
ignore-bbcode
BBCode represents simple markup, like for example highlighting important parts of a message in bold font, or italics.
This check ensures they are also found in translation.
Note
The method for detecting BBCode is currently quite simple so this check might produce false positives.
Répétition de mots¶
Added in version 4.1.
- Summary:
Le texte contient une répétition du même mot deux fois de suite :
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.duplicate.DuplicateCheck- Check identifier:
duplicate- Flag to ignore:
ignore-duplicate
Checks that no consecutive duplicate words occur in a translation. This usually indicates a mistake in the translation.
Indication
This check includes language specific rules to avoid false positives. In case it triggers falsely in your case, let us know. See Reporting issues in Weblate.
Non conforme au glossaire¶
Added in version 4.5.
- Summary:
La traduction ne respecte pas les termes du glossaire.
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.glossary.GlossaryCheck- Check identifier:
check_glossary- Flag to enable:
check-glossary- Flag to ignore:
ignore-check-glossary
This check has to be turned on using check-glossary flag (see
Customizing behavior using flags). Please consider following prior to enabling it:
It does exact string matching, the glossary is expected to contain terms in all variants.
Checking each string against glossary is expensive, it will slow down any operation in Weblate which involves running checks like importing strings or translating.
It also utilizes untranslatable glossary terms in Traduction inchangée.
Double espace¶
- Summary:
La traduction contient un double espace
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.DoubleSpaceCheck- Check identifier:
double_space- Flag to ignore:
ignore-double-space
Checks that double space is present in translation to avoid false positives on other space-related checks.
Check is false when double space is found in source meaning double space is intentional.
Parties Fluent¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
Les parties Fluent doivent correspondre
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.parts.FluentPartsCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-parts- Flag to enable:
fluent-parts- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-parts
Each Fluent Message can have an optional value (the main text content), and optional attributes, each of which is a « part » of the Message. In Weblate, all these parts appear within the same block, using Fluent-like syntax to specify the attributes. For example:
This is the Message value
.title = This is the title attribute
.alt = This is the alt attribute
This check ensures that the translated Message also has a value if the source Message has one, or no value if the source has none. This also checks that the same attributes used in the source Message also appear in the translation, with no additions.
Note
This check is not applied to Fluent Terms since Terms always have a value, and Term attributes tend to be locale-specific (used for grammar rules, etc.), and are not expected to appear in all translations.
Voir aussi
Références Fluent¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
Les références Fluent doivent correspondre
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.references.FluentReferencesCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-references- Flag to enable:
fluent-references- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-references
A Fluent Message or Term can reference another Message, Term, Attribute, or a variable. For example:
Here is a { message }, a { message.attribute } a { -term } and a { $variable }.
Within a function { NUMBER($num, minimumFractionDigits: 2) }
Generally, translated Messages or Terms are expected to contain the same references as the source, although not necessarily in the same order of appearance. So this check ensures that translations use the same references in their value as the source value, the same number of times, and with no additions. For Messages, this will also check that each Attribute in the translation uses the same references as the matching Attribute in the source.
When the source or translation contains Fluent Select Expressions, then each possible variant in the source must be matched with at least one variant in the translation with the same references, and vice versa.
Moreover, if a variable reference appears both in the Select Expression’s selector and within one of its variants, then all variants may also be considered as if they also contain that reference. The assumption being that the variant’s key may have made the reference redundant for that variant. For example:
{ $num ->
[one] an apple
*[other] { $num } apples
}
Here, for the purposes of this check, the [one] variant will also be
considered to contain the $num reference.
However, a reference within the Select Expression’s selector, which can only be a variable of a Term Attribute in Fluent’s syntax, will not by itself count as a required reference because they do not form the actual text content of the string that the end-user will see, and the presence of a Select Expression is considered locale-specific. For example:
{ -term.starts-with-vowel ->
[yes] an { -term }
*[no] a { -term }
}
Here a reference to -term.starts-with-vowel is not expected to appear in
translations, but a reference to -term is.
HTML interne de la traduction Fluent¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
La cible Fluent doit être un code HTML interne valide qui correspond à
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.inner_html.FluentTargetInnerHTMLCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-target-inner-html- Flag to enable:
fluent-target-inner-html- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-target-inner-html
This check will verify that the translated value of a Message or Term contains the same HTML elements as the source value.
First, if the source value fails the HTML interne de la source Fluent check, then this check will do nothing. Otherwise, the translated value will also be checked under the same conditions.
Second, the HTML elements found in the translated value will be compared against the HTML elements found in the source value. Two elements will match if they share the exact same tag name, the exact same attributes and values, and all their ancestors match in the same way. This check will ensure that all the elements in the source appear somewhere in the translation, with the same number of appearances, and with no additional elements added. When there are multiple elements in the value, they need not appear in the same order in the translation value.
When the source or translation contains Fluent Select Expressions, then each possible variant in the source must be matched with at least one variant in the translation with the same HTML elements, and vice versa.
When using Fluent in combination with the Fluent DOM package, this check will
ensure that the translation also includes any required data-l10n-name
elements that appear in the source, or any of the allowed inline elements like
<br>.
For example, the following source:
Source message <img data-l10n-name="icon"/> with icon
would match with:
Translated message <img data-l10n-name="icon"/> with icon
but not:
Translated message <img data-l10n-name="new-val"/> with icon
nor
Translated message <br data-l10n-name="icon"/> with no icon
Voir aussi
Syntaxe de traduction Fluent¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
Erreur de syntaxe Fluent dans la traduction
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.syntax.FluentTargetSyntaxCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-target-syntax- Flag to enable:
fluent-target-syntax- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-target-syntax
In Weblate, Fluent strings use Fluent syntax for references and variables, but also for more complex features like defining attributes and selector variants, including plurals. This check ensures that the syntax used in the translation will be valid for Fluent.
Formatted strings¶
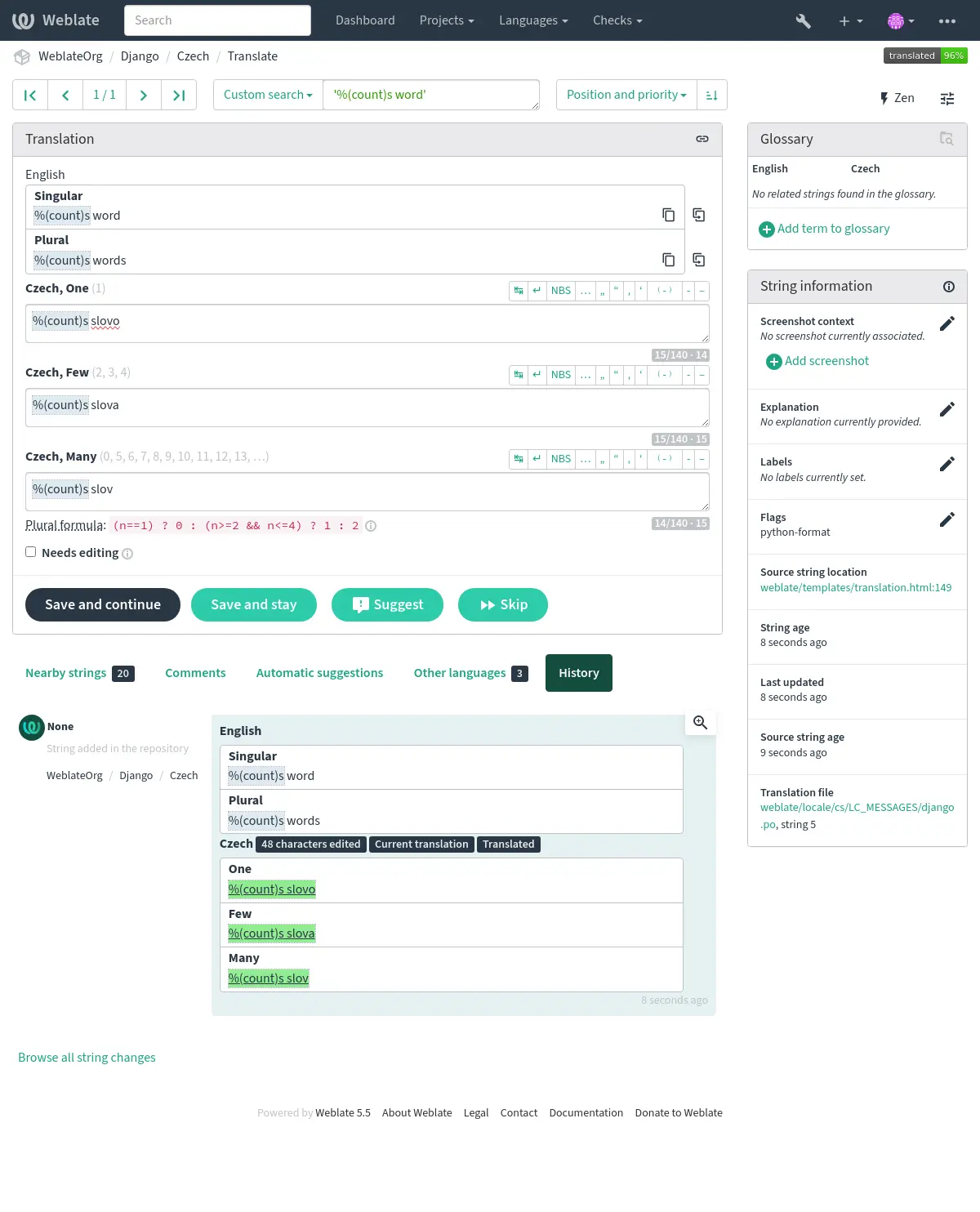
Checks that the formatting in strings is replicated between both source and translation. Omitting format strings in translation usually causes severe problems, so the formatting in strings should usually match the source.
Weblate supports checking format strings in several languages. The check is not enabled automatically, only if a string is flagged appropriately (e.g. c-format for C format). Gettext adds this automatically, but you will probably have to add it manually for other file formats or if your PO files are not generated by xgettext.
Most of the format checks allow omitting format strings for plural forms having
a single count. This allows translators to write nicer strings for these cases
(One apple instead of %d apple). Turn this off by adding strict-format flag.
The flags can be customized per string (see Additional info on source strings) or in a Configuration des composants. Having it defined per component is simpler, but it can lead to false positives in case the string is not interpreted as a formatting string, but format string syntax happens to be used.
Indication
In case specific format check is not available in Weblate, you can use generic Balises de remplacement.
Besides checking, this will also highlight the formatting strings to easily insert them into translated strings:
Chaîne d’interpolation AngularJS¶
- Summary:
Les chaînes d’interpolation AngularJS ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.angularjs.AngularJSInterpolationCheck- Check identifier:
angularjs_format- Flag to enable:
angularjs-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-angularjs-format- Named format string example:
Votre solde est {{amount}} {{ currency }}
Voir aussi
Format C¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format C ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.CFormatCheck- Check identifier:
c_format- Flag to enable:
c-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-c-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes- Position format string example:
Votre solde est %1$d %2$s
Voir aussi
Format C#¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format C# ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.CSharpFormatCheck- Check identifier:
c_sharp_format- Flag to enable:
c-sharp-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-c-sharp-format- Position format string example:
Il y a {0} pommes
Voir aussi
Modèle de littéraux ECMAScript¶
- Summary:
Les modèles littéraux ECMAScript ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.ESTemplateLiteralsCheck- Check identifier:
es_format- Flag to enable:
es-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-es-format- Interpolation example:
Il y a ${number} pommes
Voir aussi
Interpolation i18next¶
Added in version 4.0.
- Summary:
L’interpolation i18next ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.I18NextInterpolationCheck- Check identifier:
i18next_interpolation- Flag to enable:
i18next-interpolation- Flag to ignore:
ignore-i18next-interpolation- Interpolation example:
Il y a {{number}} pommes- Nesting example:
Il y a $t(number) pommes
Voir aussi
ICU MessageFormat¶
Added in version 4.9.
- Summary:
Erreurs de syntaxe et/ou incohérence de caractère de remplacement dans les chaînes ICU MessageFormat.
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.icu.ICUMessageFormatCheck- Check identifier:
icu_message_format- Flag to enable:
icu-message-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-icu-message-format- Interpolation example:
There {number, plural, one {is one apple} other {are # apples}}.
This check has support for both pure ICU MessageFormat messages as well as ICU with simple
XML tags. You can configure the behavior of this check by using icu-flags:*, either by
opting into XML support or by disabling certain sub-checks. For example, the following flag
enables XML support while disabling validation of plural sub-messages:
icu-message-format, icu-flags:xml:-plural_selectors
|
Enable support for simple XML tags. By default, XML tags
are parsed loosely. Stray |
|
Enable support for strict XML tags. All |
|
Disable highlighting placeholders in the editor. |
|
Disable requiring sub-messages to have an |
|
Skip checking that sub-message selectors match the source. |
|
Ne pas vérifier que les types de marqueurs de position correspondent à la source. |
|
Skip checking that no placeholders are present that were not present in the source string. |
|
Skip checking that no placeholders are missing that were present in the source string. |
Additionally, when strict-xml is not enabled but xml is enabled, you can use the
icu-tag-prefix:PREFIX flag to require that all XML tags start with a specific string.
For example, the following flag will only allow XML tags to be matched if they start with
<x::
icu-message-format, icu-flags:xml, icu-tag-prefix:"x:"
This would match <x:link>click here</x:link> but not <strong>this</strong>.
Format Java¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format Java ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.JavaFormatCheck- Check identifier:
java_printf_format- Flag to enable:
java-printf-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-java-printf-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes- Position format string example:
Votre solde est %1$d %2$s
Modifié dans la version 4.14: This used to be toggled by java-format flag, it was changed for consistency with GNU gettext.
Voir aussi
MessageFormat Java¶
- Summary:
La chaîne MessageFormat Java ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.JavaMessageFormatCheck- Check identifier:
java_format- Flag to enable unconditionally:
java-format- Flag to enable autodetection:
auto-java-messageformatenables check only if there is a format string in the source- Flag to ignore:
ignore-java-format- Position format string example:
Il y a {0} pommes
Modifié dans la version 4.14: This used to be toggled by java-messageformat flag, it was changed for consistency with GNU gettext.
This check validates that format string is valid for the Java MessageFormat
class. Besides matching format strings in the curly braces, it also verifies
single quotes as they have a special meaning. Whenever writing single quote, it
should be written as ''. When not paired, it is treated as beginning of
quoting and will not be shown when rendering the string.
Voir aussi
Format JavaScript¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format JavaScript ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.JavaScriptFormatCheck- Check identifier:
javascript_format- Flag to enable:
javascript-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-javascript-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes
Voir aussi
Format Lua¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format Lua ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.LuaFormatCheck- Check identifier:
lua_format- Flag to enable:
lua-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-lua-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes
Voir aussi
Format Pascal objet¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format Pascal objet ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.ObjectPascalFormatCheck- Check identifier:
object_pascal_format- Flag to enable:
object-pascal-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-object-pascal-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes
Balises de remplacement par caractères pour cent¶
Added in version 4.0.
- Summary:
Les balises de remplacement par caractères pour cent ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PercentPlaceholdersCheck- Check identifier:
percent_placeholders- Flag to enable:
percent-placeholders- Flag to ignore:
ignore-percent-placeholders- Simple format string example:
Il y a %number% pommes
Voir aussi
Format Perl avec accolades¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format Perl avec accolades ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PerlBraceFormatCheck- Check identifier:
perl_brace_format- Flag to enable:
perl-brace-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-perl-brace-format- Named format string example:
There are {number} apples
Voir aussi
Format Perl¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format Perl ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PerlFormatCheck- Check identifier:
perl_format- Flag to enable:
perl-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-perl-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes- Position format string example:
Votre solde est %1$d %2$s
Voir aussi
Format PHP¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format PHP ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PHPFormatCheck- Check identifier:
php_format- Flag to enable:
php-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-php-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes- Position format string example:
Votre solde est %1$d %2$s
Voir aussi
Formatted strings, PHP sprintf documentation, PHP Format Strings
Format d’accolade Python¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format python ne correspond pas à celui de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PythonBraceFormatCheck- Check identifier:
python_brace_format- Flag to enable:
python-brace-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-python-brace-format- Simple format string:
Il y a {} pommes- Named format string example:
Votre solde est {amount} {currency}
Voir aussi
Formatted strings, Python brace format, Python Format Strings
Format Python¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format Python ne correspond pas à celle de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.PythonFormatCheck- Check identifier:
python_format- Flag to enable:
python-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-python-format- Simple format string:
Il y a %d pommes- Named format string example:
Your balance is %(amount)d %(currency)s
Format Qt¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format Qt ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.qt.QtFormatCheck- Check identifier:
qt_format- Flag to enable:
qt-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-qt-format- Position format string example:
Il y a %1 pommes
Voir aussi
Forme plurielle Qt¶
- Summary:
La chaîne au format Qt pluriel ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.qt.QtPluralCheck- Check identifier:
qt_plural_format- Flag to enable:
qt-plural-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-qt-plural-format- Plural format string example:
Il y a %Ln pomme(s)
Voir aussi
Format Ruby¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format Ruby ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.ruby.RubyFormatCheck- Check identifier:
ruby_format- Flag to enable:
ruby-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-ruby-format- Simple format string example:
Il y a %d pommes- Position format string example:
Votre solde est %1$f %2$s- Named format string example:
Votre solde est %+.2<amount>f %<currency>s- Named template string:
Votre solde est %{amount} %{currency}
Voir aussi
Format Scheme¶
- Summary:
La chaîne de format Scheme ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.SchemeFormatCheck- Check identifier:
scheme_format- Flag to enable:
scheme-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-scheme-format- Simple format string example:
There are ~d apples
Formatage Vue I18n¶
- Summary:
Le formatage Vue I18n ne correspond pas à celui de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.VueFormattingCheck- Check identifier:
vue_format- Flag to enable:
vue-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-vue-format- Formatage nommé:
Il y a {count} pommes- Formatage Rails I18n:
Il y a %{count} pommes- Messages de paramètres régionaux liés:
@:message.dio @:message.the_world!
A déjà été traduit¶
- Summary:
Cette chaîne a été traduite par le passé
- Portée:
all strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.consistency.TranslatedCheck- Check identifier:
translated- Flag to ignore:
ignore-translated
Means a string has been translated already. This can happen when the translations have been reverted in VCS or lost otherwise.
Incohérence¶
- Summary:
Cette chaîne a différentes traductions dans ce projet ou n’est pas traduite dans certains composants.
- Portée:
all strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.consistency.ConsistencyCheck- Check identifier:
inconsistent- Flag to ignore:
ignore-inconsistent
Weblate checks translations of the same string across all translation within a project to help you keep consistent translations.
The check fails on differing translations of one string within a project. This can also lead to inconsistencies in displayed checks. You can find other translations of this string on the Other occurrences tab.
Cette vérification s’applique à tous les composants d’un projet dont l’option Permettre la propagation de la traduction est activée.
Indication
For performance reasons, the check might not find all inconsistencies, it limits number of matches.
Note
This check also fires in case the string is translated in one component and not in another. It can be used as a quick way to manually handle strings which are untranslated in some components just by clicking on the Use this translation button displayed on each line in the Other occurrences tab.
You can use Traduction automatique add-on to automate translating of newly added strings which are already translated in another component.
Voir aussi
Présence d’un caractère kashida¶
- Summary:
Les lettres décoratives kashida ne doivent pas être utilisées
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.KashidaCheck- Check identifier:
kashida- Flag to ignore:
ignore-kashida
The decorative Kashida letters should not be used in translation. These are also known as Tatweel.
Voir aussi
Liens Markdown¶
- Summary:
Les liens Markdown ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.MarkdownLinkCheck- Check identifier:
md-link- Flag to enable:
md-text- Flag to ignore:
ignore-md-link
Les liens Markdown ne correspondent pas à la source.
Voir aussi
Références Markdown¶
- Summary:
Les références de liens Markdown ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.MarkdownRefLinkCheck- Check identifier:
md-reflink- Flag to enable:
md-text- Flag to ignore:
ignore-md-reflink
Markdown link references do not match source.
Voir aussi
Syntaxe Markdown¶
- Summary:
La syntaxe Markdown ne correspond pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.MarkdownSyntaxCheck- Check identifier:
md-syntax- Flag to enable:
md-text- Flag to ignore:
ignore-md-syntax
La syntaxe Markdown ne correspond pas à la source
Voir aussi
Taille maximum de la traduction¶
- Summary:
La traduction ne doit pas dépasser la taille indiquée
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.MaxLengthCheck- Check identifier:
max-length- Flag to enable:
max-length- Flag to ignore:
ignore-max-length
Checks that translations are of acceptable length to fit available space. This only checks for the length of translation characters.
Unlike the other checks, the flag should be set as a key:value pair like
max-length:100.
Indication
This check looks at number of chars, what might not be the best metric when using proportional fonts to render the text. The Taille maximale de la traduction check does check actual rendering of the text.
The replacements: flag might be also useful to expand placeables before
checking the string.
Quand le drapeau xml-text est aussi utilisé, le calcul de la longueur ignore les balises XML.
Taille maximale de la traduction¶
- Summary:
Le texte traduit ne doit pas dépasser une taille donnée
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.render.MaxSizeCheck- Check identifier:
max-size- Flag to enable:
max-size- Flag to ignore:
ignore-max-size
Le texte rendu par la traduction ne doit pas dépasser une taille donnée. Elle fait le rendu du texte avec un retour à la ligne et vérifie s’il tient dans les limites données.
Cette vérification nécessite un ou deux paramètres - largeur maximale et nombre maximal de lignes. Si le nombre de lignes n’est pas indiqué, une seule ligne sera autorisée.
Vous pouvez également configurer la police utilisée à l’aide des directives font-* (voir Customizing behavior using flags), par exemple les drapeaux de traduction suivants indiquent que le texte rendu avec la police Ubuntu de taille 22 doit tenir sur deux lignes et 500 pixels :
max-size:500:2, font-family:ubuntu, font-size:22
Indication
You might want to set font-* directives in Configuration des composants to have the same
font configured for all strings within a component. You can override those
values per string in case you need to customize it per string.
The replacements: flag might be also useful to expand placeables before
checking the string.
Quand le drapeau xml-text est aussi utilisé, le calcul de la longueur ignore les balises XML.
Pas de correspondance \n¶
- Summary:
Le nombre de littéraux \n de la traduction n’est pas identique à celui de la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EscapedNewlineCountingCheck- Check identifier:
escaped_newline- Flag to ignore:
ignore-escaped-newline
Usually escaped newlines are important for formatting program output.
Check fails if the number of \n literals in translation does not match the source.
Incohérence de caractère deux-points¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par deux-points
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndColonCheck- Check identifier:
end_colon- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-colon
Checks that colons are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of colons is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese or Japanese).
Voir aussi
Incohérence de points de suspension¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne se finissent pas toutes les deux par des points de suspension
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndEllipsisCheck- Check identifier:
end_ellipsis- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-ellipsis
Vérifie que le caractère … est répliqué entre la source et la traduction. Cette vérification ne porte que sur les ellipses réelles (…) et non sur les trois points (...).
An ellipsis is usually rendered nicer than three dots in print, and sounds better with text-to-speech.
Voir aussi
Incohérence de point d’exclamation¶
- Summary:
La source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un point d’exclamation
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndExclamationCheck- Check identifier:
end_exclamation- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-exclamation
Checks that exclamations are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of exclamation marks is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Armenian, Limbu, Myanmar or Nko).
Voir aussi
Incohérence de point final¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un point final
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndStopCheck- Check identifier:
end_stop- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-stop
Checks that full stops are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of full stops is checked for various languages where they do not belong (Chinese, Japanese, Devanagari or Urdu).
Voir aussi
Incohérence de point d’interrogation¶
- Summary:
La source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un point d’interrogation
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndQuestionCheck- Check identifier:
end_question- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-question
Checks that question marks are replicated between both source and translation. The presence of question marks is also checked for various languages where they do not belong (Armenian, Arabic, Chinese, Korean, Japanese, Ethiopic, Vai or Coptic).
Voir aussi
Mismatched interrobang mark¶
- Summary:
Source and translation do not both end with a interrobang mark
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndInterrobangCheck- Check identifier:
end_Interrobang- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-Interrobang
Checks that interrobang marks are replicated between both source and translation. It allows the swap between « !? » and « ?! ».
Voir aussi
Incohérence de point-virgule¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un point-virgule
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndSemicolonCheck- Check identifier:
end_semicolon- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-semicolon
Checks that semicolons at the end of sentences are replicated between both source and translation.
Voir aussi
Incohérence dans les sauts de ligne¶
- Summary:
Le nombre de lignes de la traduction n’est pas identique à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.NewLineCountCheck- Check identifier:
newline-count- Flag to ignore:
ignore-newline-count
Usually newlines are important for formatting program output. Check fails if the number of new lines in translation does not match the source.
Pluriels manquants¶
- Summary:
Certaines formes plurielles n’ont pas été traduites
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.consistency.PluralsCheck- Check identifier:
plurals- Flag to ignore:
ignore-plurals
Checks that all plural forms of a source string have been translated. Specifics on how each plural form is used can be found in the string definition.
Failing to fill in plural forms will in some cases lead to displaying nothing when the plural form is in use.
Balises de remplacement¶
- Summary:
Balises de remplacement absentes de la traduction
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.placeholders.PlaceholderCheck- Check identifier:
placeholders- Flag to enable:
placeholders- Flag to ignore:
ignore-placeholders
Modifié dans la version 4.3: Vous pouvez utiliser des expressions rationnelles comme substitut.
Modifié dans la version 4.13: With the case-insensitive flag, the placeholders are not case-sensitive.
Translation is missing some placeholders. These are either extracted from the
translation file or defined manually using placeholders flag, more can be
separated with colon, strings with space can be quoted:
placeholders:$URL$:$TARGET$:"some long text"
In case you have some syntax for placeholders, you can use a regular expression:
placeholders:r"%[^% ]%"
You can also have case insensitive placeholders:
placeholders:$URL$:$TARGET$,case-insensitive
Voir aussi
Espacement de ponctuation¶
- Summary:
Espace insécable manquante devant le signe de ponctuation double
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.PunctuationSpacingCheck- Check identifier:
punctuation_spacing- Flag to ignore:
ignore-punctuation-spacing
Checks that there is non breakable space before double punctuation sign (exclamation mark, question mark, semicolon and colon). This rule is used only in a few selected languages like French or Breton, where space before double punctuation sign is a typographic rule.
Voir aussi
Expression rationnelle¶
- Summary:
La traduction ne respecte pas l’expression rationnelle
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.placeholders.RegexCheck- Check identifier:
regex- Flag to enable:
regex- Flag to ignore:
ignore-regex
Translation does not match regular expression. The expression is either extracted from the
translation file or defined manually using regex flag:
regex:^foo|bar$
Traduction réutilisée¶
Added in version 4.18.
- Summary:
Différentes chaînes sont traduites de manière identique.
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.consistency.ReusedCheck- Check identifier:
reused- Flag to ignore:
ignore-reused
Check that fails if the same translation is used on different source strings. Such translations can be intentional, but can also confuse users.
Pluriel identique¶
- Summary:
Les traductions au singulier et au pluriel sont identiques
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.consistency.SamePluralsCheck- Check identifier:
same-plurals- Flag to ignore:
ignore-same-plurals
Check that fails if some plural forms are duplicated in the translation. In most languages they have to be different.
Nouvelle ligne au début¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne commencent pas toutes les deux par un saut de ligne
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.BeginNewlineCheck- Check identifier:
begin_newline- Flag to ignore:
ignore-begin-newline
Newlines usually appear in source strings for good reason, omissions or additions can lead to formatting problems when the translated text is put to use.
Voir aussi
Espaces au début¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne commencent pas toutes les deux par le même nombre d’espaces
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.BeginSpaceCheck- Check identifier:
begin_space- Flag to ignore:
ignore-begin-space
A space in the beginning of a string is usually used for indentation in the interface and thus important to keep.
Saut de ligne à la fin¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un saut de ligne
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndNewlineCheck- Check identifier:
end_newline- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-newline
Newlines usually appear in source strings for good reason, omissions or additions can lead to formatting problems when the translated text is put to use.
Voir aussi
Espace à la fin¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la traduction ne finissent pas toutes les deux par un espace
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.EndSpaceCheck- Check identifier:
end_space- Flag to ignore:
ignore-end-space
Checks that trailing spaces are replicated between both source and translation.
Trailing space is usually utilized to space out neighbouring elements, so removing it might break layout.
Traduction inchangée¶
- Summary:
La chaîne source et la chaîne traduite sont identiques
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.same.SameCheck- Check identifier:
same- Flag to ignore:
ignore-same
Happens if the source and corresponding translation strings is identical, down to at least one of the plural forms. Some strings commonly found across all languages are ignored, and various markup is stripped. This reduces the number of false positives.
This check can help find strings mistakenly untranslated.
The default behavior of this check is to exclude words from the built-in
blacklist from the checking. These are words which are frequently not being
translated. This is useful to avoid false positives on short strings, which
consist only of single word which is same in several languages. This blacklist
can be disabled by adding strict-same flag to string or component.
Modifié dans la version 4.17: With check-glossary flag (see Non conforme au glossaire), the
untranslatable glossary terms are excluded from the checking.
HTML non sûr¶
- Summary:
La traduction utilise du code HTML non sûr
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.SafeHTMLCheck- Check identifier:
safe-html- Flag to enable:
safe-html- Flag to ignore:
ignore-safe-html
The translation uses unsafe HTML markup. This check has to be enabled using
safe-html flag (see Customizing behavior using flags). There is also accompanied
autofixer which can automatically sanitize the markup.
Indication
When md-text flag is also used, the Markdown style links are also allowed.
Voir aussi
The HTML check is performed by the Ammonia library.
URL¶
- Summary:
La traduction ne contient pas d’URL
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.URLCheck- Check identifier:
url- Flag to enable:
url- Flag to ignore:
ignore-url
The translation does not contain an URL. This is triggered only in case the unit is marked as containing URL. In that case the translation has to be a valid URL.
Balisage XML¶
- Summary:
Les balises XML dans la traduction ne correspondent pas à la source
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.XMLTagsCheck- Check identifier:
xml-tags- Flag to ignore:
ignore-xml-tags
This usually means the resulting output will look different. In most cases this is not a desired result from changing the translation, but occasionally it is.
Checks that XML tags are replicated between both source and translation.
The check is automatically enabled for XML like strings. You might need to add
xml-text flag in some cases to force turning it on.
Note
This check is disabled by the safe-html flag as the HTML cleanup done by
it can produce HTML markup which is not valid XML.
Syntaxe XML¶
- Summary:
Cette traduction n’est pas un XML valide
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.markup.XMLValidityCheck- Check identifier:
xml-invalid- Flag to ignore:
ignore-xml-invalid
The XML markup is not valid.
The check is automatically enabled for XML like strings. You might need to add
xml-text flag in some cases to force turning it on.
Note
This check is disabled by the safe-html flag as the HTML cleanup done by
it can produce HTML markup which is not valid XML.
Espace sans chasse¶
- Summary:
La traduction contient un caractère espace sans chasse
- Portée:
translated strings
- Check class:
weblate.checks.chars.ZeroWidthSpaceCheck- Check identifier:
zero-width-space- Flag to ignore:
ignore-zero-width-space
Zero-width space (<U+200B>) characters are used to break messages within words (word wrapping).
As they are usually inserted by mistake, this check is triggered once they are present in translation. Some programs might have problems when this character is used.
Voir aussi
Source checks¶
Source checks can help developers improve the quality of source strings.
Points de suspension¶
- Summary:
Cette chaîne contient trois points (…) au lieu du caractère points de suspension (…)
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.source.EllipsisCheck- Check identifier:
ellipsis- Flag to ignore:
ignore-ellipsis
This fails when the string uses three dots (...) when it should use an ellipsis character (…).
Using the Unicode character is in most cases the better approach and looks better rendered, and may sound better with text-to-speech.
Voir aussi
HTML interne de la source Fluent¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
La source Fluent doit être du HTML interne valide
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.inner_html.FluentSourceInnerHTMLCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-source-inner-html- Flag to enable:
fluent-source-inner-html- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-source-inner-html
Fluent is often used in contexts where the value for a Message (or Term) is
meant to be used directly as .innerHTML (rather than .textContent) for
some HTML element. For example, when using the Fluent DOM package.
The aim of this check is to predict how the value will be parsed as inner HTML, assuming a HTML5 conforming parser, to catch cases where there would be some « unintended » loss of the string, without being too strict about technical parsing errors that do not lead to a loss of the string.
This check is applied to the value of Fluent Messages or Terms, but not their Attributes. For Messages, the Fluent Attributes are often just HTML attribute values, so can be arbitrary strings. For Terms, the Fluent Attributes are often language properties that can only be referenced in the selectors of Fluent Select Expressions.
Generally, most Fluent values are not expected to contain any HTML markup. Therefore, this check does not expect or want translators and developers to have to care about strictly avoiding any technical HTML5 parsing errors (let alone XHTML parsing errors). Instead, this check will just want to warn them when they may have unintentionally opened a HTML tag or inserted a character reference.
Moreover, for the Fluent values that intentionally contain HTML tags or character references, this check will verify some « good practices », such as matching closing and ending tags, valid character references, and quoted attribute values. In addition, whilst the HTML5 specification technically allows for quite arbitrary tag and attribute names, this check will restrain them to some basic ASCII values that should cover the standard HTML5 element tags and attributes, as well as allow some custom element or attribute names. This is partially to ensure that the user is using HTML intentionally.
Examples:
Valeur |
Warns? |
Reason |
|---|---|---|
|
oui |
The |
|
non |
The |
|
oui |
Missing a closing tag. |
|
oui |
|
|
non |
Custom element tag with a matching closing tag. |
|
non |
|
|
non |
|
|
oui |
The attribute value is not quoted. |
|
oui |
Non-ASCII tag name. |
|
oui |
The |
|
non |
The character reference seems to be intentional. |
|
oui |
The |
|
oui |
The character reference is not valid. |
|
oui |
The Fluent variable may unintentionally become a tag. |
|
oui |
The Fluent variable may unintentionally become a character reference. |
Note
This check will not ensure the inner HTML is safe or sanitized, and is not
meant to protect against malicious attempts to alter the inner HTML.
Moreover, it should be remembered that Fluent variables and references may
expand to arbitrary strings, so could expand to arbitrary HTML unless they
are escaped. As an exception, a < or & character before a Fluent
reference will trigger this check since even an escaped value could lead to
unexpected results.
Note
The Fluent DOM package has further limitations, such as allowed tags and attributes, which this check will not enforce.
Voir aussi
Syntaxe Fluent source¶
Added in version 5.0.
- Summary:
Erreur de syntaxe Fluent dans le source
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.fluent.syntax.FluentSourceSyntaxCheck- Check identifier:
fluent-source-syntax- Flag to enable:
fluent-source-syntax- Flag to ignore:
ignore-fluent-source-syntax
In Weblate, Fluent strings use Fluent syntax for references and variables, but also for more complex features like defining attributes and selector variants, including plurals. This check ensures that the syntax used in source will be valid for Fluent.
Syntaxe ICU MessageFormat¶
Added in version 4.9.
- Summary:
Erreurs de syntaxe dans les chaines ICU MessageFormat.
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.icu.ICUSourceCheck- Check identifier:
icu_message_format_syntax- Flag to enable:
icu-message-format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-icu-message-format
Voir aussi
Ancienne chaîne non traduite¶
Added in version 4.1.
- Summary:
Cette chaîne n’a pas été traduite depuis longtemps
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.source.LongUntranslatedCheck- Check identifier:
long_untranslated- Flag to ignore:
ignore-long-untranslated
When the string has not been translated for a long time, it can indicate a problem in a source string making it hard to translate.
Plusieurs vérifications en échec¶
- Summary:
Les traductions dans plusieurs langues ont des vérifications échouées
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.source.MultipleFailingCheck- Check identifier:
multiple_failures- Flag to ignore:
ignore-multiple-failures
Numerous translations of this string have failing quality checks. This is usually an indication that something could be done to improve the source string.
This check failing can quite often be caused by a missing full stop at the end of a sentence, or similar minor issues which translators tend to fix in translation, while it would be better to fix it in the source string.
Multiples variables non nommées¶
Added in version 4.1.
- Summary:
Il y a plusieurs variables non nommées dans la chaîne, ce qui rend impossible leur réorganisation par les traducteurs
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.format.MultipleUnnamedFormatsCheck- Check identifier:
unnamed_format- Flag to ignore:
ignore-unnamed-format
There are multiple unnamed variables in the string, making it impossible for translators to reorder them.
Consider using named variables instead to allow translators to reorder them.
Non pluralisé¶
- Summary:
Cette chaîne est utilisée comme un pluriel, sans utiliser les formes plurielles
- Portée:
chaînes sources
- Check class:
weblate.checks.source.OptionalPluralCheck- Check identifier:
optional_plural- Flag to ignore:
ignore-optional-plural
The string is used as a plural, but does not use plural forms. In case your translation system supports this, you should use the plural aware variant of it.
For example with Gettext in Python it could be:
from gettext import ngettext
print(ngettext("Selected %d file", "Selected %d files", files) % files)