Proyectos de traducción¶
Organización de traducción¶
Weblate organizes translatable VCS content of project/components into a tree-like structure. You can additionally organize components within a project using categories.
The bottom level object is Configuración de proyectos, which should hold all translations belonging together (for example translation of an application in several versions and/or accompanying documentation).
The middle level is optionally created by Categoría. The categories can be nested to achieve more complex structure.
On the level above, Configuración de componentes, which is actually the component to translate, you define the VCS repository to use, and the mask of files to translate.
Above Configuración de componentes there are individual translations, handled automatically by Weblate as translation files (which match Máscara de archivos defined in Configuración de componentes) appear in the VCS repository.
Weblate supports a wide range of translation formats (both bilingual and monolingual ones) supported by Translate Toolkit, see Formatos de archivo admitidos.
Nota
You can share cloned VCS repositories using URL internos de Weblate. Using this feature is highly recommended when you have many components sharing the same VCS. It improves performance and decreases required disk space.
Añadir proyectos y componentes de traducción¶
Based on your permissions, new translation projects and components can be created. It is always permitted for users with the Add new projects permission, and if your instance uses billing (e.g. like https://hosted.weblate.org/ see Facturación), you can also create those based on your plans allowance from the user account that manages billing.
Consejo
To grant every user permission to create new projects create new Asignación automática de los equipos for the Project creators team.
Puede ver su plan de facturación actual en una página separada:
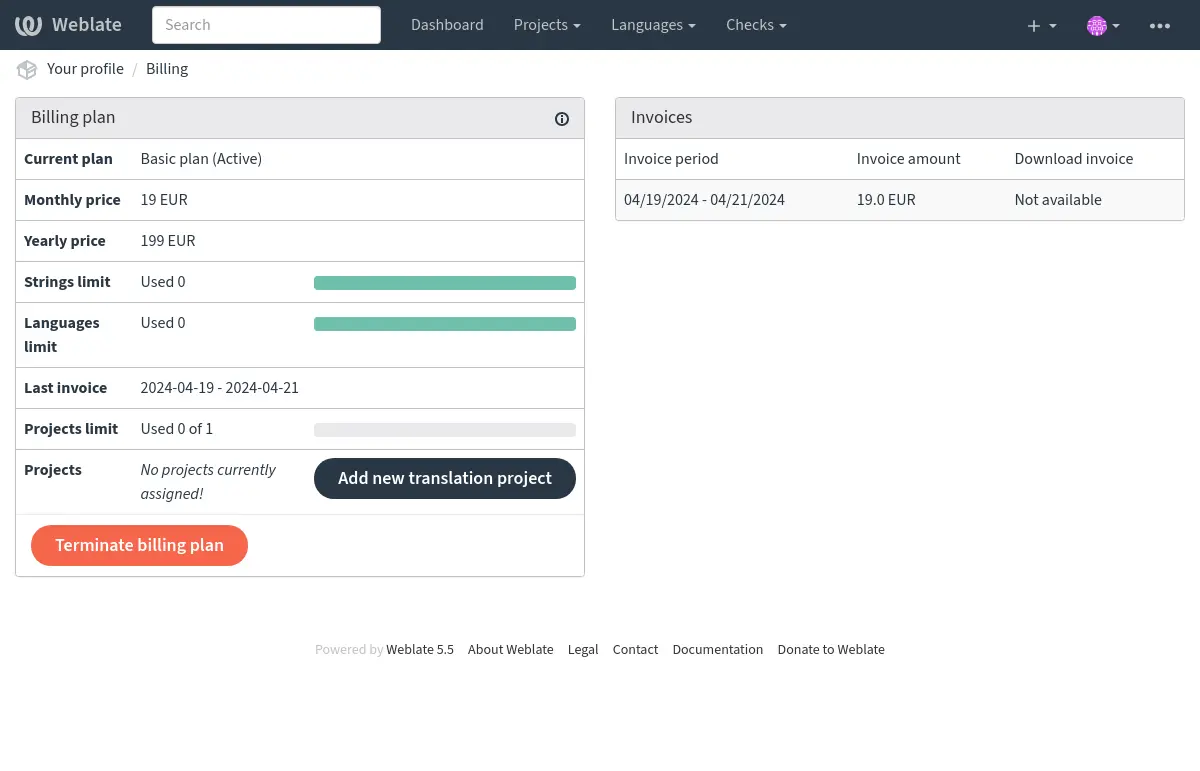
The project creation can be initiated from there, or using the menu in the navigation bar, filling in basic info about the translation project to complete addition of it:
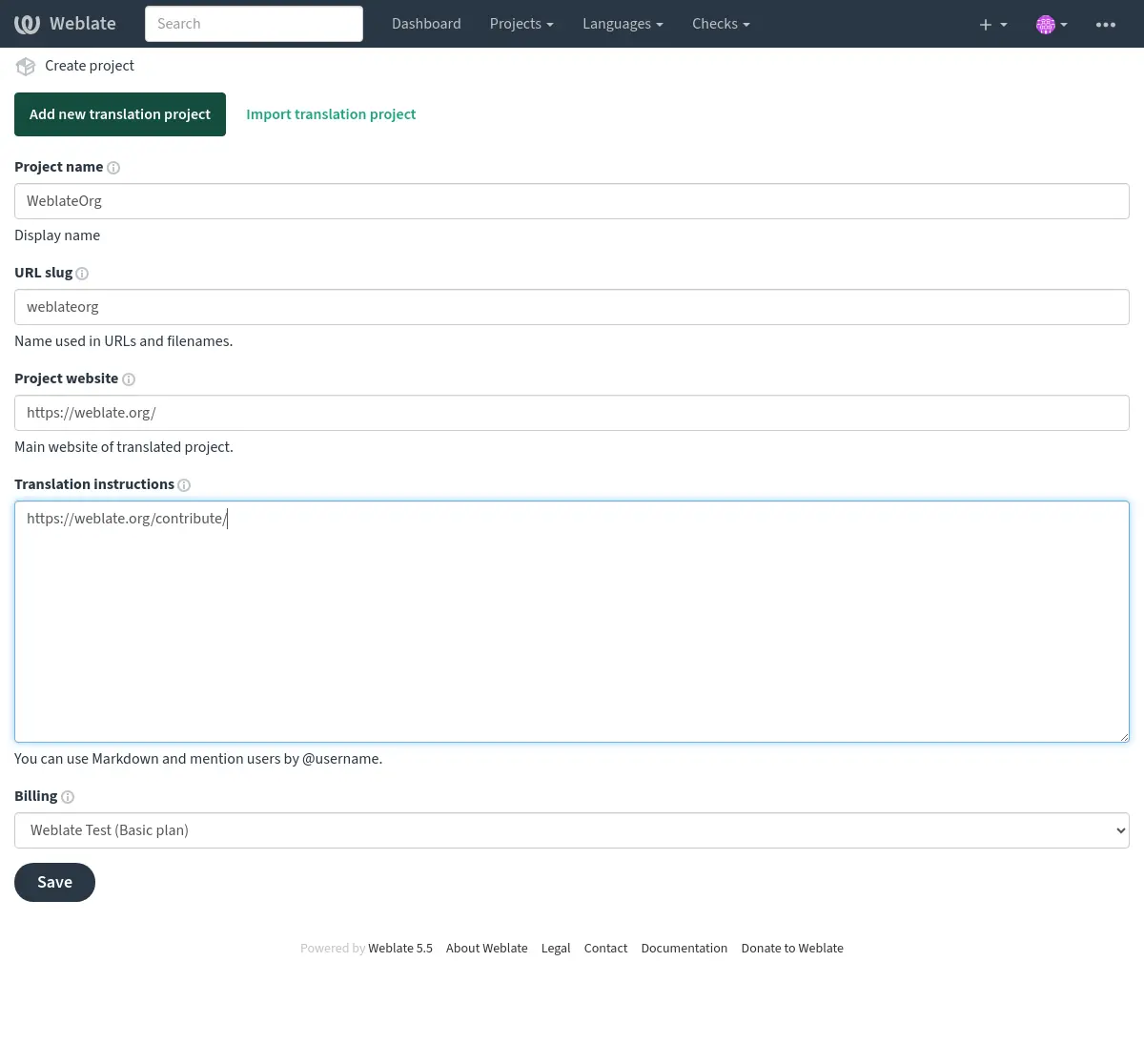
After creating the project, you are taken directly to the project page:
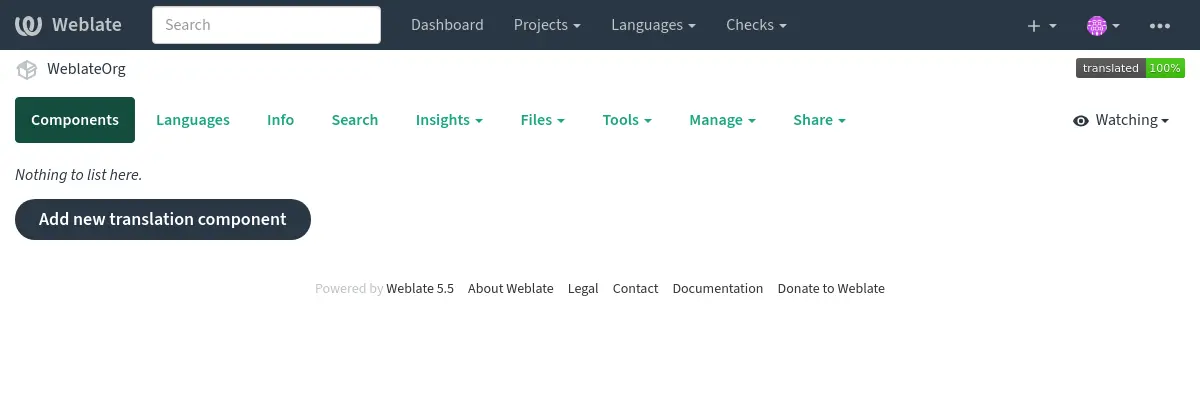
Creating a new translation component can be initiated via a single click there. The process of creating a component is multi-staged and automatically detects most translation parameters. There are several approaches to creating component:
- Desde control de versiones
Crea el componente a partir de un repositorio de control de versiones remoto.
- Desde componente existente
Creates additional component to existing one by choosing different files.
- Rama adicional
Creates additional component to existing one, just for different branch.
- Cargar archivos de traducción
Upload translation files to Weblate in case you do not have version control or do not want to integrate it with Weblate. You can later update the content using the web interface or API REST de Weblate.
- Traducir documento
Suba un solo documento o archivo de traducción y tradúcelo.
- Comenzar de cero
Create blank translation project and add strings manually.
Once you have existing translation components, you can also easily add new ones for additional files or branches using same repository.
Primero debe suplir el nombre y la ubicación del repositorio:
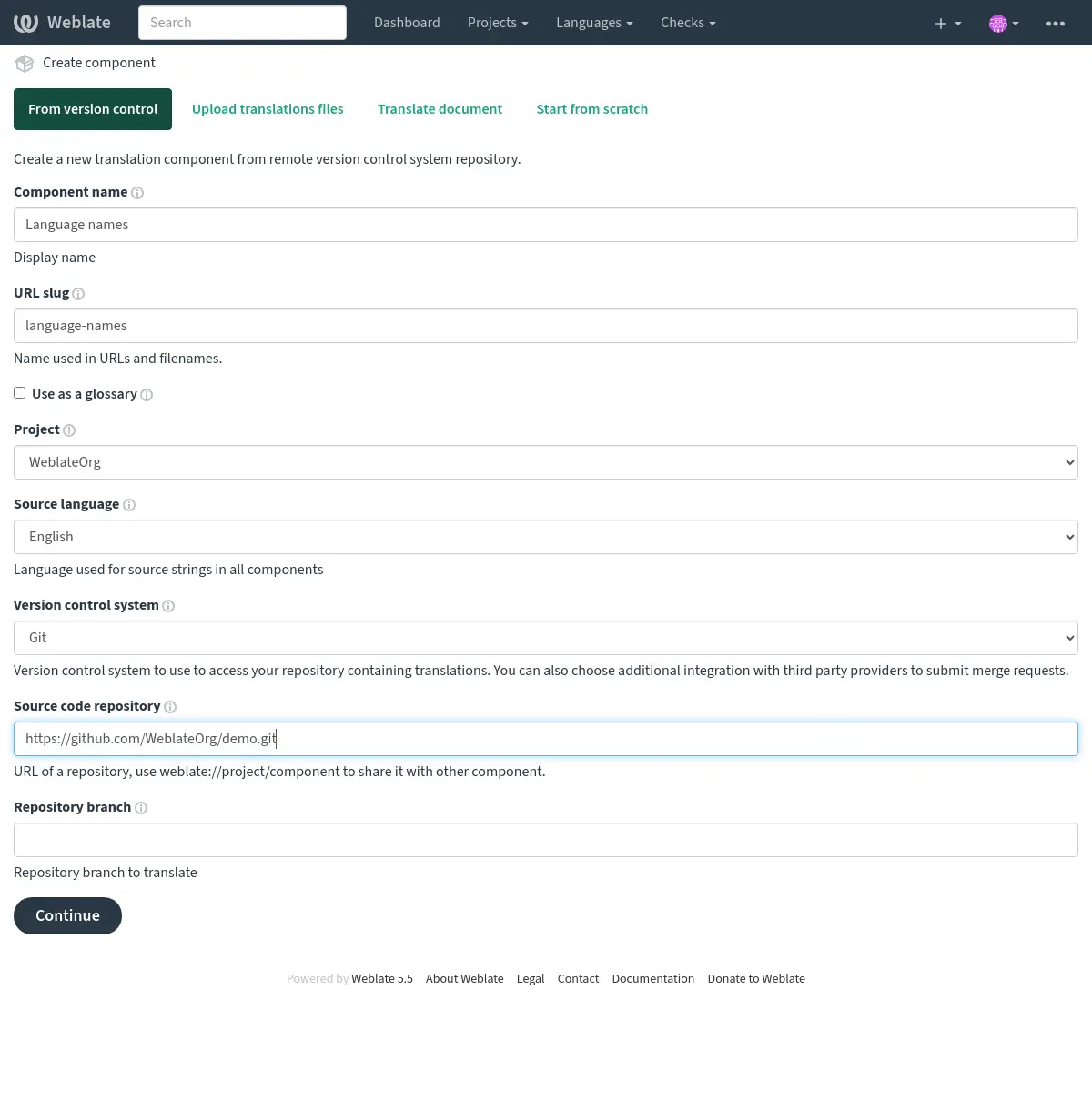
En la próxima página verá una lista de recursos traducibles detectados:
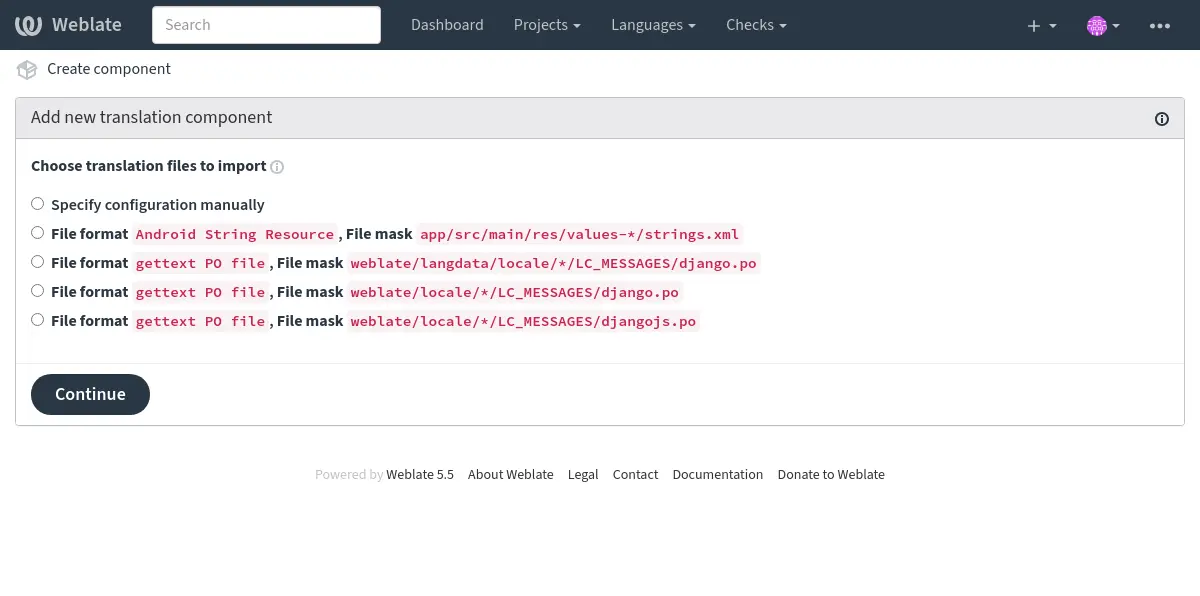
Como último paso, revise la información del componente de traducción y supla datos opcionales:
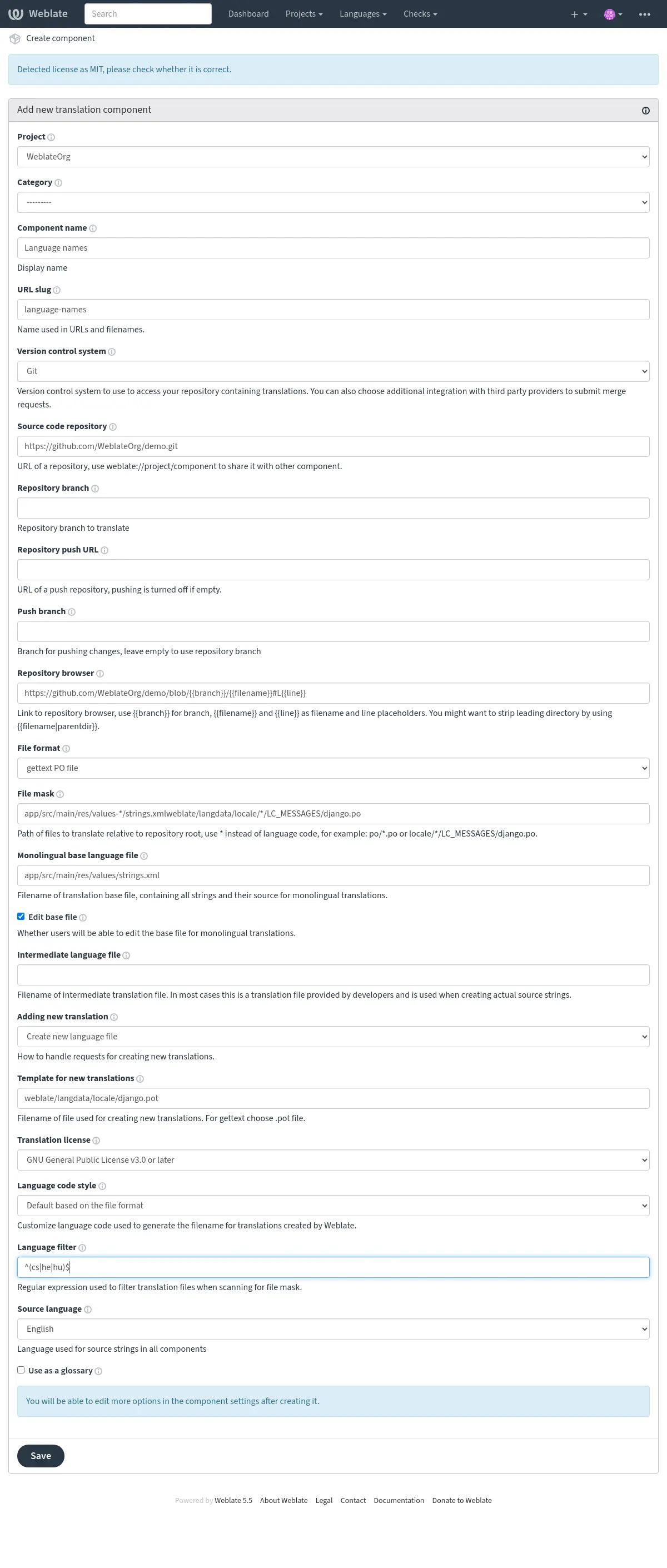
Configuración de proyectos¶
Create a translation project and then add a new component for translation in it. The project is like a shelf, in which real translations are stacked. All components in the same project share suggestions and their dictionary; the translations are also automatically propagated through all components in a single project (unless turned off in the component configuration), see Memoria de traducción.
Ver también
These basic attributes set up and inform translators of a project:
Nombre del proyecto¶
Verbose project name, used to display the project name.
Ver también
«Slug» del URL¶
Project name suitable for URLs.
Sitio web del proyecto¶
URL where translators can find more info about the project.
This is a required parameter unless turned off by WEBSITE_REQUIRED.
Instrucciones de traducción¶
Text describing localization process in the project, and any other information useful for translators. Markdown can be used for text formatting or inserting links.
Definir cabecera «Language-Team»¶
Whether Weblate should manage the Language-Team header (this is a
GNU gettext PO (Portable Object) only feature right now).
Control de acceso¶
Configure per project access control, see Control de acceso al proyecto for more details.
El valor predeterminado se puede cambiar mediante :setting: DEFAULT_ACCESS_CONTROL.
Activar revisiones¶
Enable review workflow for translations, see Revisores dedicados.
Ver también
Activar revisiones de origen¶
Enable review workflow for source strings, see Source strings reviews.
Ver también
Activar actuadores¶
Whether unauthenticated Actuadores de notificación are to be used for this repository.
Alias de idiomas¶
Definir el mapeo de los códigos de idioma al importar las traducciones a Weblate. Utilícelo cuando los códigos del idioma sean inconsistentes en sus repositorios y quiera obtener una vista consistente en Weblate o en caso de que quiera utilizar una nomenclatura no estándar para sus archivos de traducción.
The typical use case might be mapping American English to English: en_US:en
Multiple mappings to be separated by comma: en_GB:en,en_US:en
Using non standard code: ia_FOO:ia
Consejo
The language codes are mapped when matching the translation files and the matches are case sensitive, so ensure you use the source language codes in same form as used in the filenames.
Configuración de componentes¶
A component is a grouping of something for translation. You enter a VCS repository location and file mask for which files you want translated, and Weblate automatically fetches from this VCS, and finds all matching translatable files.
Ver también
You can find some examples of typical configurations in the Formatos de archivo admitidos.
Nota
Se recomienda mantener los componentes de traducción en un tamaño razonable: divida la traducción por cualquier cosa que tenga sentido en su caso (aplicaciones o complementos individuales, capítulos de libros o sitios web).
Weblate puede manejar con facilidad traducciones de decenas de miles de cadenas, pero es más difícil distribuir el trabajo y coordinar los traductores al utilizar componentes de tales dimensiones.
Should the language definition for a translation be missing, an empty definition is created and named as «cs_CZ (generated)». You should adjust the definition and report this back to the Weblate authors, so that the missing languages can be included in next release.
The component contains all important parameters for working with the VCS, and for getting translations out of it:
Nombre de componente¶
Verbose component name, used to display the component name.
«Slug» del componente¶
Component name suitable for URLs.
Proyecto del componente¶
Configuración de proyectos where the component belongs.
Sistema de control de versiones¶
VCS to use, see Integración de control de versiones for details.
Ver también
Repositorio de código fuente¶
VCS repository used to pull changes.
Ver también
See Accessing repositories for more details on specifying URLs.
Consejo
This can either be a real VCS URL or weblate://project/component
indicating that the repository should be shared with another component.
See URL internos de Weblate for more details.
URL de envío al repositorio¶
Repository URL used for pushing. The behavior of this depends on Sistema de control de versiones, and this is in more detail covered in Enviar cambios efectuados en Weblate.
For linked repositories, this is not used and setting from linked component applies.
Ver también
See Accessing repositories for more details on how to specify a repository URL and Enviar cambios efectuados en Weblate for more details on pushing changes from Weblate.
Explorador del repositorio¶
URL of repository browser used to display source files (location of used messages). When empty, no such links will be generated. You can use Marcación de plantilla.
For example on GitHub, use something like:
https://github.com/WeblateOrg/hello/blob/{{branch}}/{{filename}}#L{{line}}
In case your paths are relative to different folder (path contains ..), you
might want to strip leading directory by parentdir filter (see
Marcación de plantilla):
https://github.com/WeblateOrg/hello/blob/{{branch}}/{{filename|parentdir}}#L{{line}}
URL de repositorio exportado¶
URL where changes made by Weblate are exported. This is important when Localización continua is not used, or when there is a need to manually merge changes. You can use Git exporter to automate this for Git repositories.
Rama del repositorio¶
Which branch to checkout from the VCS, and where to look for translations.
For linked repositories, this is not used and setting from linked component applies.
Rama a la que enviar¶
Branch for pushing changes, leave empty to use Rama del repositorio.
For linked repositories, this is not used and setting from linked component applies.
Nota
This is currently only supported for Git, GitLab and GitHub, it is ignored for other VCS integrations.
Ver también
Máscara de archivos¶
Mask of files to translate, including path. It should include one «*» replacing language code (see Definiciones de idioma for info on how this is processed). In case your repository contains more than one translation file (e.g. more gettext domains), you need to create a component for each of them.
For example po/*.po or locale/*/LC_MESSAGES/django.po.
En caso de que el nombre del archivo contenga caracteres especiales como [, ], éstos deben escaparse como [[] o []].
Máscara del archivo de la captura de pantalla¶
This feature allows the discovery and updating of screenshots through screenshot file masks, using paths from the VCS repository. This operates at the component level and necessitates the use of an asterisk «*» to replace the screenshot file name.
Allowed formats are WebP, JPEG, PNG, APNG and GIF.
Note:
The file mask and screenshot file mask are not related. Configure them separately.
It is a manual job to link a discovered screenshot in a component to a specific translation key.
Por ejemplo:
Let’s assume your VCS repository has a structure like this:
component_A
└── docs
├── image1.png
└── image2.jpg
For component_A, you want to allow discovery and updates of PNG screenshots.
You’d set the screenshot file mask for component_A as component_A/docs/*.png.
This means any PNG images under docs in component_A can be discovered and updated.
So, if you want to update image1.png, the new screenshot you provide should be named image1.png,
matching the existing filename, and stored under component_A/docs/.
Archivo de base monolingüe¶
Base file containing string definitions for Componentes monolingües.
Editar archivo de base¶
Whether to allow editing strings in the Archivo de base monolingüe.
Archivo de idioma intermediario¶
Intermediate language file for Componentes monolingües. In most cases this is a translation file provided by developers and is used when creating actual source strings.
When set, the source strings are based on this file, but all other languages are based on Archivo de base monolingüe. In case the string is not translated into the source language, translating to other languages is prohibited. This provides Quality gateway for the source strings.
Plantilla para traducciones nuevas¶
Base file used to generate new translations.
Keep this field empty for most of the monoligual formats. Those are typically able to start from an empty file.
Choose
.potfile with GNU gettext PO files.Choose blank file without translations, if you have one.
Choose Archivo de base monolingüe for monolingual formats that need a full set of keys present.
Choose Archivo de base monolingüe for document translations.
Choose any translation file for others.
Template file can be the same as the base file in most cases.
Consejo
In many monolingual formats Weblate starts with empty file by default. Use this in case you want to have all strings present with empty value when creating new translation.
Formato de archivo¶
Translation file format, see also Formatos de archivo admitidos.
Dirección para informar de errores en las cadenas de origen¶
Email address used for reporting upstream bugs. This address will also receive notification about any source string comments made in Weblate.
With the GNU gettext PO (Portable Object) format, this address is also saved by Weblate in the Report-Msgid-Bugs-To header of the file.
Permitir propagación de traducciones¶
You can turn off propagation of translations to this component from other components within same project. This really depends on what you are translating, sometimes it’s desirable to have make use of a translation more than once.
It’s usually a good idea to turn this off for monolingual translations, unless you are using the same IDs across the whole project.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_TRANSLATION_PROPAGATION.
Activar sugerencias¶
Whether translation suggestions are accepted for this component.
Ver también
Votar sugerencias¶
Turns on vote casting for suggestions, see Votar sugerencias.
Ver también
Aceptar sugerencias automáticamente¶
Automatically accept voted suggestions, see Votar sugerencias.
Ver también
Indicadores de traducción¶
Customization of quality checks and other Weblate behavior, see Personalizar el comportamiento mediante indicadores.
Comprobaciones obligatorias¶
List of checks which can not be ignored, see Forzar comprobaciones.
Nota
Enforcing the check does not automatically enable it, you still should enabled it using Personalizar el comportamiento mediante indicadores in Indicadores de traducción or Información adicional sobre las cadenas de origen.
Licencia de la traducción¶
License of the translation (does not need to be the same as the source code license).
Acuerdo de contribuidor¶
Acuerdo de usuario que debe aprobarse antes de que un usuario pueda traducir este componente.
Adición de traducciones nuevas¶
How to handle requests for creation of new languages. Available options:
- Contactar a responsables
User can select desired language and the project maintainers will receive a notification about this. It is up to them to add (or not) the language to the repository.
- Apuntar al URL con instrucciones de traducción
User is presented a link to page which describes process of starting new translations. Use this in case more formal process is desired (for example forming a team of people before starting actual translation).
- Crear archivo de idioma nuevo
User can select language and Weblate automatically creates the file for it and translation can begin.
- Desactivar adición de traducciones nuevas
There will be no option for user to start new translation.
Consejo
The project admins can add new translations even if it is disabled here when it is possible (either Plantilla para traducciones nuevas or the file format supports starting from an empty file).
Gestionar cadenas¶
Added in version 4.5.
Configures whether users in Weblate will be allowed to add new strings and remove existing ones. Adjust this to match your localization workflow - how the new strings are supposed to be introduced.
For bilingual formats, the strings are typically extracted from the source code (for example by using xgettext) and adding new strings in Weblate should be disabled (they would be discarded next time you update the translation files). In Weblate you can manage strings for every translation and it does not enforce the strings in all translations to be consistent.
For monolingual formats, the strings are managed only on source language and are automatically added or removed in the translations. The strings appear in the translation files once they are translated.
Consejo
You might want to turn on Editar archivo de base together with Manage strings for monolingual formats.
Estilo de código de idioma¶
Personalice el código de idioma utilizado para generar el nombre de archivo de las traducciones creadas por Weblate.
Nota
Weblate recognizes any of the language codes when parsing translation files, following settings only influences how new files are created.
- Basado en el formato de archivo predefinido
Depende del formato de archivo; en la mayoría se utiliza POSIX.
- Estilo POSIX con guion bajo como separador
Typically used by gettext and related tools, produces language codes like
pt_BR.- Estilo POSIX con guion bajo como separador; incluye el código de país
POSIX style language code including the country code even when not necessary (for example
cs_CZ).- El estilo POSIX que utiliza el guión bajo como separador, incluido el código del país (en minúsculas)
POSIX style language code including the country code even when not necessary (lowercase) (for example
cs_cz).- Estilo BCP con guion como separador
Typically used on web platforms, produces language codes like
pt-BR.- Estilo BCP con guion como separador; incluye el código de país
BCP style language code including the country code even when not necessary (for example
cs-CZ).- Estilo BCP que utiliza el guión como separador, códigos de idiomas heredados
Uses legacy codes for Chinese and BCP style notation.
- Estilo BCP con guión como separador, en minúsculas
BCP style notation, all in lower case (for example
cs-cz).- Estilo a los metadatos de la App Store de Apple
Style suitable for uploading metadata to Apple App Store.
- Estilo de los metadatos de Google Play
Style suitable for uploading metadata to Google Play Store.
- Estilo Android
Only used in Android apps, produces language codes like
pt-rBR.- Estilo Linux
Locales as used by Linux, uses legacy codes for Chinese and POSIX style notation.
Estilo de fusión¶
You can configure how updates from the upstream repository are handled. The actual implementation depends on VCS, see Integración de control de versiones.
- Cambiar base («rebase»)
Rebases Weblate commits on top of upstream repository on update. This provides clean history without extra merge commits.
Rebasing can cause you trouble in case of complicated merges, so carefully consider whether or not you want to enable them.
You might need to enable force pushing by choosing Git con envío forzado as Sistema de control de versiones, especially when pushing to a different branch.
- Fusionar
Upstream repository changes are merged into Weblate one. This setting utilizes fast-forward when possible. This is the safest way, but might produce a lot of merge commits.
- Fusionar sin avance rápido
Upstream repository changes are merged into Weblate one with doing a merge commit every time (even when fast-forward would be possible). Every Weblate change will appear as a merge commit in Weblate repository.
Default value can be changed by DEFAULT_MERGE_STYLE.
Confirmar, agregar, eliminar, fusionar, agregar y fusionar mensajes de la solicitud¶
Message used when committing a translation, see Marcación de plantilla.
El valor predeterminado se puede cambiar :configurando:`DEFAULT_ADD_MESSAGE`, :configurando:`DEFAULT_ADDON_MESSAGE`, :configurando:`DEFAULT_COMMIT_MESSAGE`, :configurando:`DEFAULT_DELETE_MESSAGE`, :configurando:`DEFAULT_MERGE_MESSAGE`, :configurando:`DEFAULT_PULL_MESSAGE`.
Enviar al consignar¶
Whether committed changes should be automatically pushed to the upstream repository. When enabled, the push is initiated once Weblate commits changes to its underlying repository (see Consignas diferidas). To actually enable pushing Repository push URL has to be configured as well.
Antigüedad de cambios por consignar¶
Sets how old (in hours) changes have to be before they are committed by
background task or the commit_pending management command. All
changes in a component are committed once there is at least one change
older than this period.
Default value can be changed by COMMIT_PENDING_HOURS.
Consejo
There are other situations where pending changes might be committed, see Consignas diferidas.
Bloquear al producirse un error¶
Locks the component (and linked components, see URL internos de Weblate) upon the first failed push or merge into its upstream repository, or pull from it. This avoids adding another conflicts, which would have to be resolved manually.
The component will be automatically unlocked once there are no repository errors left.
Idioma del código fuente¶
Language used for source strings. Change this if you are translating from something else than English.
Consejo
In case you are translating bilingual files from English, but want to be able to do fixes in the English translation as well, choose English (Developer) as a source language to avoid conflict between the name of the source language and the existing translation.
For monolingual translations, you can use intermediate translation in this case, see Archivo de idioma intermediario.
Filtro de idioma¶
Expresión regular utilizada para filtrar la traducción al buscar una máscara del archivo. Se puede utilizar para limitar la lista de idiomas gestionados por Weblate.
Nota
You need to list language codes as they appear in the filename.
Some examples of filtering:
Descripción del filtro |
Expresión regular |
|---|---|
Solo los idiomas seleccionados |
|
Excluir idiomas |
|
Filter two letter codes only |
|
Excluir archivos no lingüísticos |
|
Incluir todos los archivos (predeterminado) |
|
Expresión regular de variantes¶
Regular expression used to determine the variants of a string, see Variantes de cadenas.
Nota
La mayoría de los campos pueden ser editados por los propietarios o administradores del proyecto en la interfaz de Weblate.
Prioridad¶
Se ofrecen primero a los traductores los componentes con mayor prioridad.
Distinto en la versión 4.15: This now also affects ordering of matched glossary terms.
Acceso restringido¶
Nota
Esta función no está disponible en Hosted Weblate.
By default the component is visible to anybody who has access to the project, even if the person can not perform any changes in the component. This makes it easier to keep translation consistency within the project.
Restricting access at a component, or component-list level takes over access permission to a component, regardless of project-level permissions. You will have to grant access to it explicitly. This can be done through granting access to a new user group and putting users in it, or using the default custom or private access control groups.
The default value can be changed in DEFAULT_RESTRICTED_COMPONENT.
Consejo
This applies to project admins as well — please ensure you will not loose access to the component after toggling the status.
Utilizar como glosario¶
Added in version 4.5.
Permite la utilización de este componente como glosario. Puede definir cómo se mostrará en las listas mediante Color de glosario.
El glosario será accesible en todos los proyectos definidos por Compartir en proyectos.
Se recomienda la activación de Gestionar cadenas en los glosarios para permitir la adición de palabras nuevas.
Ver también
Color de glosario¶
Display color for a glossary used when showing word matches.
Categoría¶
Categories are there to give structure to components within a project. You can nest them to achieve a more complex structure.
Marcación de plantilla¶
Weblate uses simple markup language in several places where text rendering is needed. It is based on The Django template language, so it can be quite powerful.
Actualmente se utiliza en:
Commit message formatting, see Configuración de componentes
- Varios complementos
Las variables siguientes están disponibles en las plantillas de componente:
{{ language_code }}Código de idioma
{{ language_name }}Nombre del idioma
{{ component_name }}Nombre de componente
{{ component_slug }}«Slug» del componente
{{ project_name }}Nombre del proyecto
{{ project_slug }}«Slug» del proyecto
{{ url }}URL de traducción
{{ filename }}Nombre de archivo de traducción
{{ stats }}Translation stats, this has further attributes, examples below.
{{ stats.all }}Total strings count
{{ stats.fuzzy }}Count of strings needing review
{{ stats.fuzzy_percent }}Percent of strings needing review
{{ stats.translated }}Translated strings count
{{ stats.translated_percent }}Translated strings percent
{{ stats.allchecks }}Number of strings with failing checks
{{ stats.allchecks_percent }}Percent of strings with failing checks
{{ author }}Author of current commit, available only in the commit scope.
{{ addon_name }}Name of currently executed add-on, available only in the add-on commit message.
The following variables are available in the repository browser or editor templates:
{{branch}}current branch
{{line}}line in file
{{filename}}filename, you can also strip leading parts using the
parentdirfilter, for example{{filename|parentdir}}
Consejo
In some places additional variables can be available, see Detección de componentes.
You can combine them with filters:
{{ component|title }}
You can use conditions:
{% if stats.translated_percent > 80 %}Well translated!{% endif %}
Hay una etiqueta adicional disponible para sustituir caracteres:
{% replace component "-" " " %}
You can combine it with filters:
{% replace component|capfirst "-" " " %}
There are also additional filter to manipulate with filenames:
Directory of a file: {{ filename|dirname }}
File without extension: {{ filename|stripext }}
File in parent dir: {{ filename|parentdir }}
It can be used multiple times: {{ filename|parentdir|parentdir }}
…and other Django template features.
Importing speed¶
Fetching VCS repository and importing translations to Weblate can be a lengthy process, depending on size of your translations. Here are some tips:
Optimize configuration¶
The default configuration is useful for testing and debugging Weblate, while for a production setup, you should do some adjustments. Many of them have quite a big impact on performance. Please check Puesta en marcha de entorno de producción for more details, especially:
Configure Celery for executing background tasks (see Tareas en segundo plano con Celery)
Check resource limits¶
If you are importing huge translations or repositories, you might be hit by resource limitations of your server.
Check the amount of free memory, having translation files cached by the operating system will greatly improve performance.
Disk operations might be bottleneck if there is a lot of strings to process—the disk is pushed by both Weblate and the database.
Additional CPU cores might help improve performance of background tasks (see Tareas en segundo plano con Celery).
Disable unneeded checks¶
Some quality checks can be quite expensive, and if not needed,
can save you some time during import if omitted. See CHECK_LIST for
info on configuration.
Creación automática de componentes¶
In case your project has dozen of translation files (e.g. for different
gettext domains, or parts of Android apps), you might want to import them
automatically. This can either be achieved from the command-line by using
import_project or import_json, or by installing the
Detección de componentes add-on.
To use the add-on, you first need to create a component for one translation file (choose the one that is the least likely to be renamed or removed in future), and install the add-on on this component.
For the management commands, you need to create a project which will contain all
components and then run import_project or
import_json.
Ver también